Fig. 6. Overview of human Elongator complex-mediated reaction.
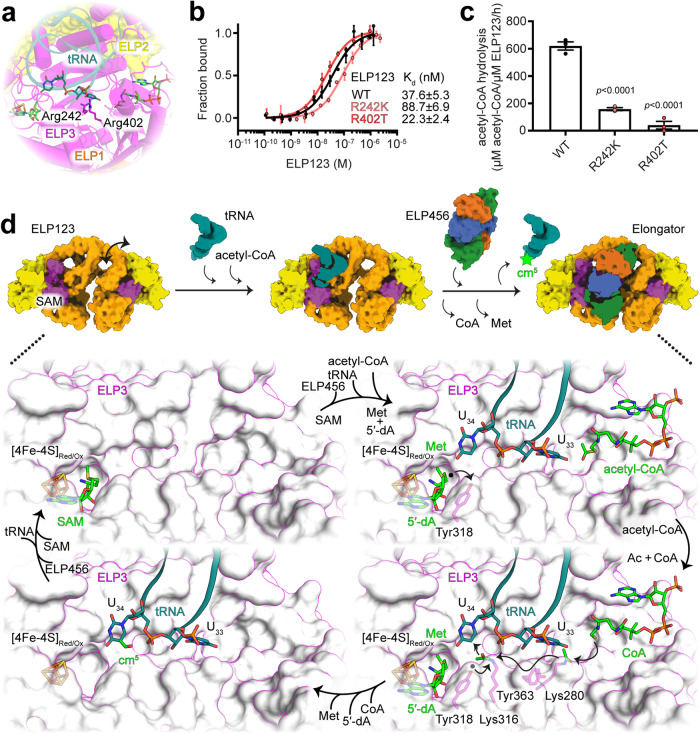
a Mapping of the analyzed clinically relevant ELP3 variants. b MST measurements with calculated Kd values for clinically relevant ELP3 variants bound to tRNAGlnUUG. n = 3 (independent experiments). Data are presented as mean values ± SEM. c Acetyl-CoA hydrolysis rates of clinical-relevant ELP3 variants in the presence of tRNAGlnUUG, n = 3 (independent experiments). Statistical analysis: one-way ANOVA with Dunnett’s multiple comparisons test. Statistically significant differences are indicated. Data are presented as mean values ± SEM. d Proposed mechanism of cm5 addition by human Elongator. While S-Adenosylmethionine (SAM) is in place, the tRNA binds to ELP123 and triggers the recruitment of acetyl-CoA. SAM is cleaved into 5ʹ-dA and methionine (MET) and the radical reaches Tyr318. From the other side, U33 triggers the acetyl-CoA hydrolysis and the acetyl group (Ac) travels through the channel with the help of Lys280, Tyr363 to reach Lys316. From there the Tyr318 radical and the acetyl group are close enough for addition on U34. ELP456 facilitates displacement of the modified tRNA by binding to the ELP123. Source data are provided as a Source Data file.