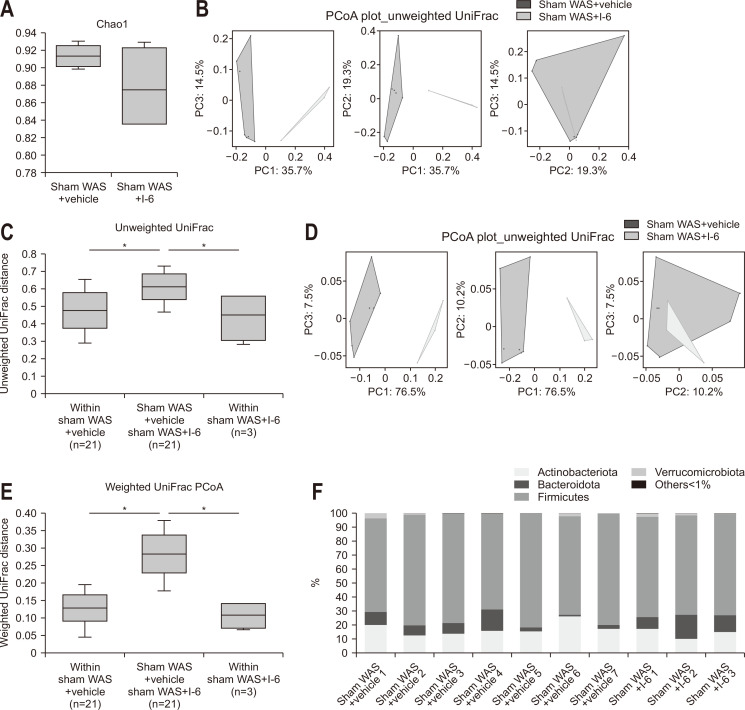
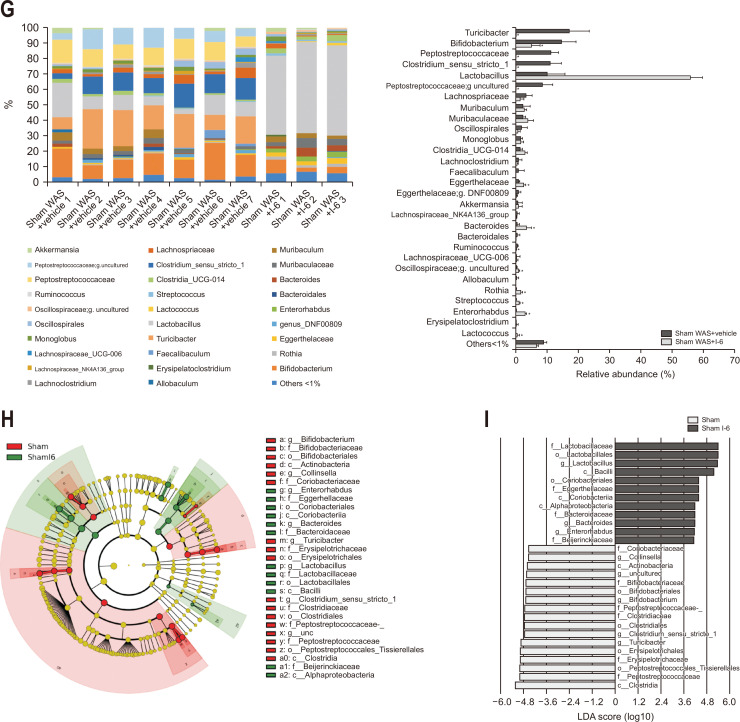
Fig. 4.
Strain I-6 treatment altered the β-diversity and intestinal bacterial abundance in rats. (A) Effect of strain I-6 on α-diversity. (B) Effect of strain I-6 on β-diversity, unweighted Unifrac principal coordinate analysis (PCoA) plot. (C) Quantification and comparison of the effect of strain I-6 on β-diversity, weighted Unifrac PCoA plot. (D) Effect of strain I-6 on β-diversity, weighted Unifrac PCoA plot. (E) Quantification and comparison of the effect of strain I-6 on β-diversity, weighted Unifrac PCoA plot. (F, G) Effect of strain I-6 on the relative intestinal bacterial abundance, phylum level and gene level. Linear discriminant analysis (LDA) effect size (LEfSe) was used to calculate the taxa that best discriminated between the sham water avoidance stress (WAS)+vehicle group and the sham WAS+I-6 group. (H) Expressed in a cladogram, taxa that reached a linear discriminant analysis score (log10) of >2.0 are highlighted and labeled accordingly. (I) LDA score>4.0 at taxonomic levels. The rats were divided into a sham WAS+vehicle group (n=7) and a sham WAS+I-6 group (n=3). Results are expressed as means±SDs. *p<0.01 compared with the sham WAS+vehicle group.