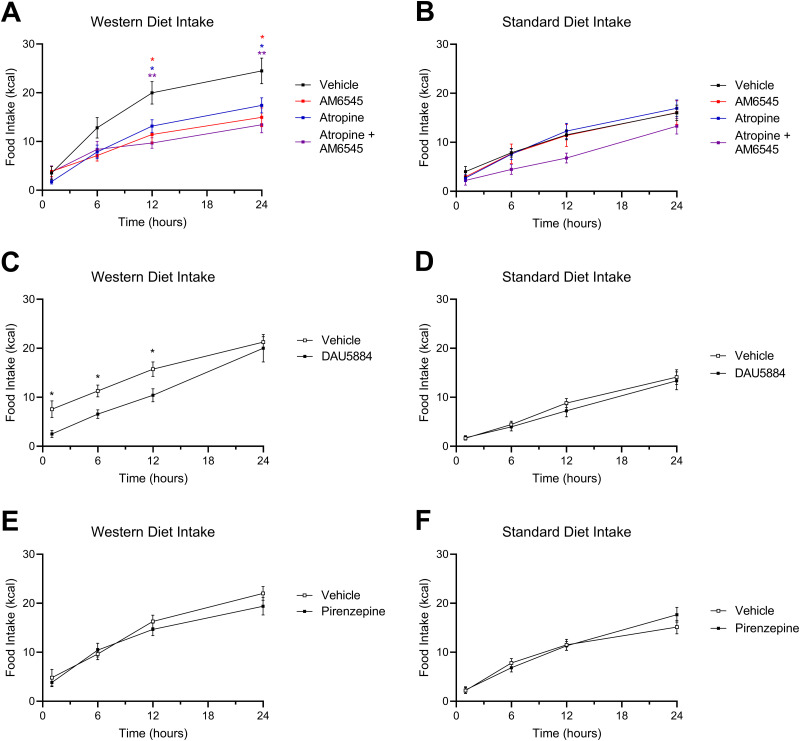
Figure 7.
Anticholinergics inhibit food intake in DIO mice. A, AM6545 (10 mg/kg), ATR (2 mg/kg), or a combination of AM6545 + ATR reduced caloric intake for up to 24 h in Western diet-fed (WD) mice (time × drug interaction, F(9,158) = 4.639; p < 0.0001; drug main effect F(3,54) = 4.560; p = 0.0064; 12 h vehicle vs 12 h ATR p = 0.0175, 12 h vehicle vs 12 h AM6545 p = 0.0143, 12 h vehicle vs 12 h combination p = 0.0020, 24 h vehicle vs 24 h ATR p = 0.0301, 24 h vehicle vs 24 h AM6545 p = 0.0145, 24 h vehicle vs 24 h combination p = 0.0049; two-way ANOVA followed by Holm–Sidak's multiple-comparisons test). B, AM6545, ATR, or both drugs in combination did not affect caloric intake in standard diet-fed (SD) mice (time × drug interaction, F(9,164) = 0.9117; p = 0.5165; time main effect F(2.103,115.0) = 142.4; p < 0.0001; drug main effect F(3,56) = 1.69; p = 0.1799; two-way ANOVA). C, DAU5884 (2 mg/kg) reduced caloric intake for up to 12 h in WD mice (time × drug interaction, F(3,84) = 1.239; p = 0.3009; drug main effect F(1,28) = 6.750; p = 0.0148; 1 h vehicle vs 1 h DAU p = 0.0358, 6 h vehicle vs 6 h DAU p = 0.0168, 12 h vehicle vs 12 h DAU p = 0.0358; two-way ANOVA followed by Holm–Sidak's multiple-comparisons test). D, DAU5884 did not affect caloric intake in SD mice for 24 h (time × drug interaction, F(3,70) = 0.5839; p = 0.6276; drug main effect F(1,24) = 0.2090; p = 0.6517; two-way ANOVA). E, PIR (2 mg/kg) did not affect caloric intake in WD mice (time × drug interaction, F(3,80) = 1.526; p = 0.2140; drug main effect F(1,28) = 0.1463; p = 0.7050; two-way ANOVA). F, PIR did not affect caloric intake in standard diet-fed mice (time × drug interaction, F(3,79) = 1.781; p = 0.1576; drug main effect F(1,28) = 0.07073; p = 0.7922; two-way ANOVA). All data are presented as mean ± SEM, n = 15–16; *p < 0.05, **p < 0.01.