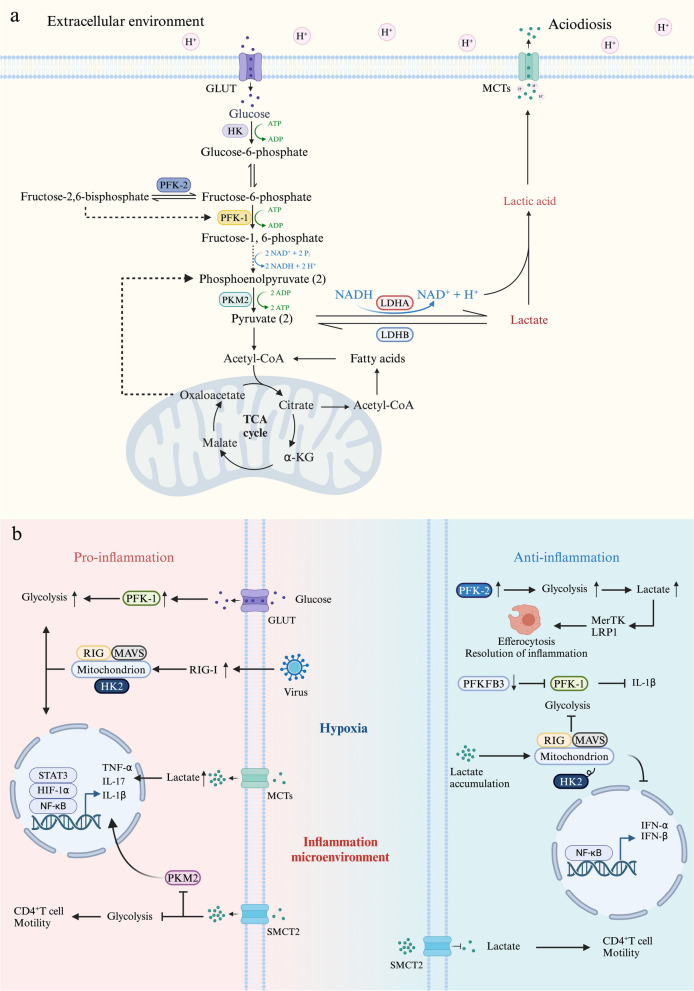
Fig. 1.
a Key enzymes the participate in glycolysis. In the inflammatory microenvironment, the rate of glycolysis increases to facilitate rapid energy production, resulting in an increase in lactate synthesis. On the one hand, the accumulation of lactate acidifies the extracellular space, thus impairing immune cell viability and functionality. On the other hand, lactate serves as a crucial carbon source for immune cells and acts as a vital metabolic fuel during the later stages of inflammation. b Lactate-related receptors in the inflammatory microenvironment. Lactate metabolism plays crucial roles during proinflammatory and anti-inflammatory processes in maintaining inflammation-environmental homeostasis. Lactate is transported by specific receptors to exert proinflammatory or anti-inflammatory effects in the inflammatory microenvironment.