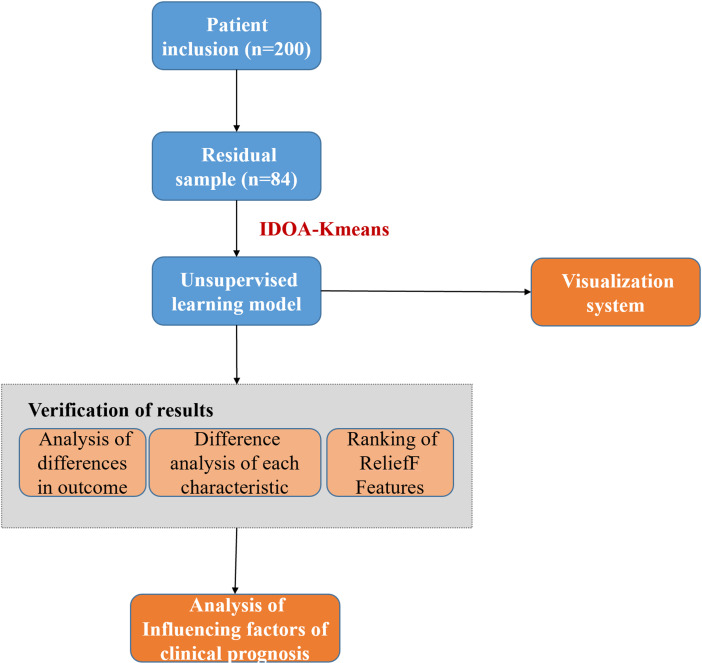
Figure 1. The technical flowchart of this study.
(1) Data collection: First, we collected the required data from appropriate sources, which may include demographic information, clinical indicators, laboratory test results, and other content. (2) Feature extraction: Next, we process the collected data and extract features related to the research purpose. (3) Improved algorithm and synchronous optimization: To improve the initial point selection dependency of the traditional k-means algorithm, we introduce the swarm intelligence algorithm and conduct synchronous optimization to achieve the task of feature filtering and initial point optimization. (4) Feature selection and cluster analysis: After optimization, we further conducted feature selection to identify features that had a significant impact on the prognosis. Next, we use the improved k-means algorithm to cluster the data and divide the samples into different clusters. (5) Model training and evaluation: Based on clustering analysis, we use the selected features to train the prediction model and evaluate the model to evaluate its performance and predictive ability. The cases (80 cases) that meet the inclusion criteria after screening of COVID-19 patients (200 cases) are called residual samples. Residual samples refer to the leftover samples after the initial analysis or processing steps have been completed.