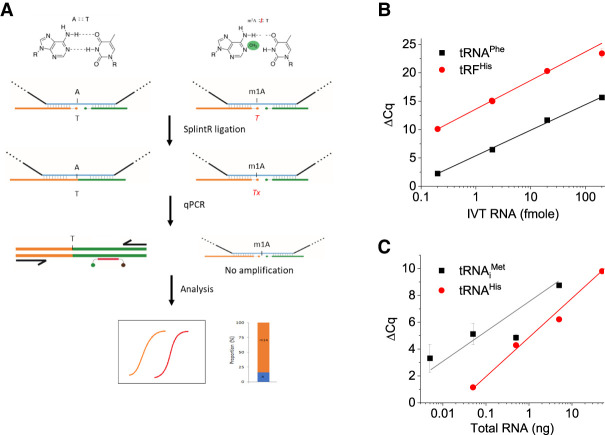
FIGURE 1.
TL-qPCR schematics and quantitative and sensitive detection of synthetic and biological tRNAs. (A) The basic design of measuring m1A in tRNA. The 5 linkers (5lkrT) with phosphorylated T at the 5′ end binds to complementary RNA template containing A or m1A at the same position. SplintR ligase ligates the 5lkrT linker and the 3′ linker at the joint position where the T pairs with A, but not with m1A. The ligated 5lkrT product is then used as template in qPCR using fluorescent probes. Comparing the difference of Cq value from A and m1A after normalization to controls, the m1A levels in the RNA sample are obtained. (B) Detection of model tRNA. ΔCq value between RNA sample and water control using 0.2–200 fmol in vitro transcript of yeast tRNAPhe (black) or a synthetic human tRNAHis fragment (red) using the 5lkrT linker in ligation. ΔCq values have a nice linear correlation with the log values of input amounts. (C) Detection of human tRNAiMet and tRNAHis in HEK293T total RNA. ΔCq value between RNA sample and water control. tRNAiMet or tRNAHis is still detectable at 5 or 50 pg total RNA input, respectively.