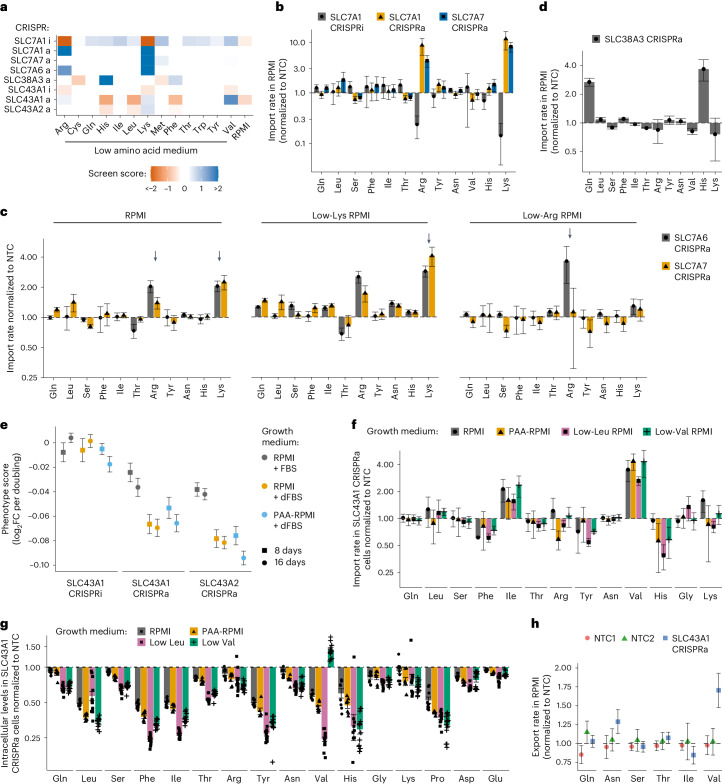
Fig. 3. SLC43A1/LAT3 is a net exporter of large neutral amino acids.
a, Scores obtained in CRISPRi/a screens in low amino acid and in RPMI. b, SLC7A1 CRISPRi/a and SLC7A7 CRISPRa specifically alter the import of arginine and lysine in K562 cells in RPMI. c, SLC7A7 CRISPRa increases the import of lysine when lysine is present in the medium at growth-limiting concentrations. SLC7A6 CRISPRa increases the import of arginine and lysine in all conditions tested. The arrows highlight the import of Arg and Lys in RPMI, import of Lys in low-Lys conditions and import of Arg in low-Arg conditions. d, SLC38A3 CRISPRa increases import of histidine and glutamine into K562 cells in RPMI. e, CRISPRa of SLC43A1 and SLC43A2 induces a proliferation defect in K562 over a range of conditions (RPMI with regular FBS, RPMI with dialyzed FBS (dFBS), and RPMI modified such that amino acids match human plasma levels (PAA-RPMI)). Data are the mean ± s.e.m. of two biological replicates each with six technical replicates. f, CRISPRa of SLC43A1 increases import of isoleucine and valine into K562 cells. g, CRISPRa of SLC43A1 decreases intracellular levels of large neutral amino acids in K562 cells. Levels were determined from import assays in f (n = 7 biologically independent samples; data are mean ± s.e.m.). h, CRISPRa of SLC43A1 increases the export rate of valine from K562 cells cultured in RPMI. In b–d,f and h, the rates were determined from a linear regression of n = 6 biologically independent samples. The data represent the slope ± SE normalized to a non-targeting control (NTC). Source numerical data are available in Source data.