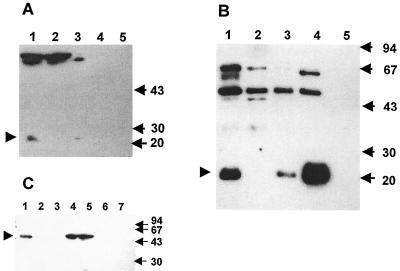
FIG. 2.
Determination of the cellular localization of PncA and PzaA in mycobacteria by Western blot analysis. Western blotting was carried out as described in Materials and Methods. The locations of PncA and PzaA are indicated by arrowheads, and the sizes are given in kilodaltons. (A) Detection of PncA in M. tuberculosis strains. Lanes: 1, cell lysate from wild-type H37Rv; 2, cell lysate from the pncA::hyg mutant; 3, cell lysate from the pncA-complemented mutant, pncA::hyg::pAIncA; 4, culture filtrate protein precipitate from wild-type H37Rv; 5, culture filtrate protein precipitate from pncA::hyg::pAIncA. (B) Detection of PncA in M. smegmatis strains. Lanes: 1, cell lysate from mc2155(pOncA); 2, cell lysate from wild-type mc2155; 3, cell lysate from mc2155::pHncA; 4, cell lysate from mc2155(pOppncA); 5, culture filtrate protein precipitate from mc2155::pHncA. (C) Detection of PzaA in M. tuberculosis and M. smegmatis strains. Lanes: 1, cell lysate from wild-type mc2155; 2, cell lysate from the pzaA::aph mutant; 3, cell lysate from wild-type H37Rv; 4 and 5, cell lysate from the pzaA-complemented mutant, pncA::hyg::pAIam; 6, culture filtrate protein precipitate from the pncA::hyg::pAIam mutant; 7, culture filtrate protein precipitate from wild-type mc2155.