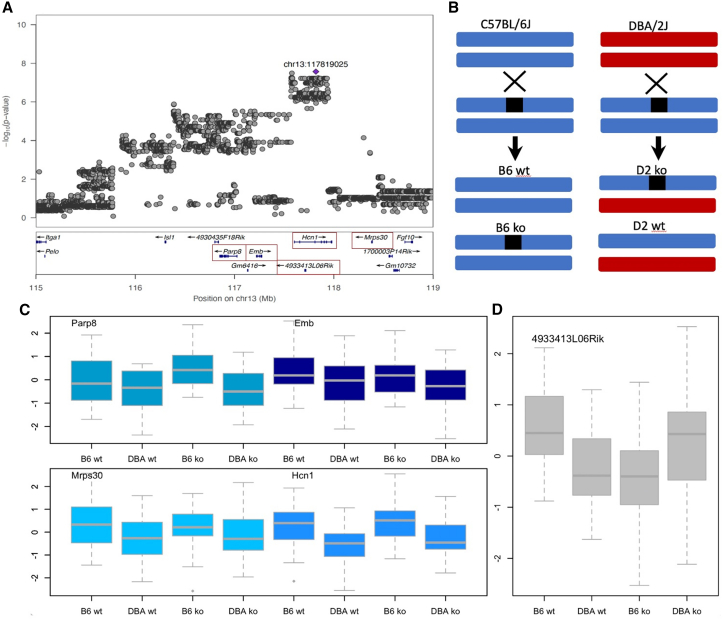
Figure 2.
Quantitative complementation of five genes at a locus on chromosome 13 for cue fear conditioning
(A) QTL regional information from LocusZoom.59 The top part shows the association results from a meta-analysis, with the position of the highest-scoring variant annotated in purple. The vertical scale is the negative logarithm (base 10) of the association p value. The bottom section gives the location and orientation of genes at the locus. A red box identifies each gene used in the quantitative complementation tests.
(B) Design of the quantitative complementation test. Black boxes indicate the knockout (KO) allele, and strain is indicated by color, where blue is C57BL/6J and red is DBA/2J. An “X” indicates a cross between the named groups above and below the X, and an arrow points to the progeny of each cross. The four groups used in the quantitative complementation test are wild-type C57BL/6J (B6 WT), heterozygote KOs (B6 KOs), an F1 from crossing DBA/2J to C57BL/6J (D2 WT), and the F1 KO by DBA/2J (D2 KO).
(C) Results of quantitative complementation testing of four annotated genes in the region. The vertical axis is the quantile normalized duration of freezing to a cue from the fear-conditioning test. The horizontal axis lists the groups of mices used. Groups are B6.WT: WT C57BL/6J; B6.KO: heterozygote KOs on C57BL/6J; D2.WT: F1 from crossing DBA/2J to C57BL/6J; D2.KO: the F1 from crossing the KO onto DBA/2J. These genes were not significant by quantitative complementation (Table 1).
(D) Results of the quantitative complementation test for the long non-coding RNA 4933413L06Rik. The axes labels are the same as in (C). The difference between these groups yielded a significant interaction result in the quantitative complementation test (Table 1).