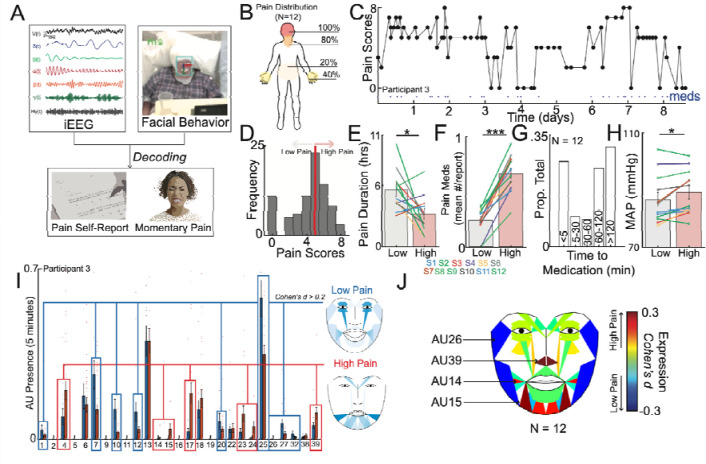
Figure 1: Naturalistic study design and inpatient tracking of acute pain states.
A) The naturalistic paradigm comprises recording intermittent verbal pain self-report along with simultaneous intracranial electroencephalography (iEEG) and patient videos. Transient episodes of momentary pain are manually annotated based on video review. iEEG spectro-spatial features and quantitative facial dynamics are used to decode acute pain states. B) Group-level anatomical distribution of self-reported pain locations (N = 12). C) Variations in pain scores for an example participant over the course of nine days. Dots denote time when a pain medication was given. D) Histogram of all recorded pain scores for the same example participant. The median value was used to denote the threshold to define low versus high acute pain states. E) Amount of time spent in low versus high pain states based on consecutive pain reports that are of the same state. Participants overall spent less time in the high pain state compared to the low pain state (paired t-test; t(11): 2.6, P=0.02). F) More pain medications were given during the high pain state compared to the low pain state (paired t-test; t(11): 10.1, P<.001). G) Distribution of pain medication timing with relations to time of pain report. H) Higher mean arterial pressure (MAP) across participants was observed in the high pain state as compared to the low pain state (paired t-test: t(11): 2.7, P=0.02). I) Proportion of different AUs encountered during high versus low pain states for an example participant. Certain AUs denoting a positive affect are more expressed during low pain states whereas AUs associated with negative affect are more expressed during high pain states. J) Consensus AUs (d > 0.2) across participants which were differentially expressed between acute pain states. Colors represent the effect size between high versus low pain states. *Denotes P < 0.05, **P < 0.01 and *** P < 0.001.