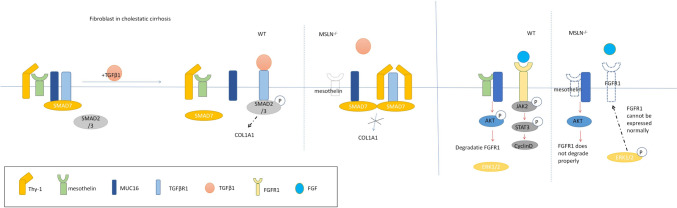
Fig. 5.
The mechanism of MUC16 in cholestatic hepatic fibrosis. In wild type (WT) aPFs in cholestatic fibrosis, Thy-1 and MUC16 interact with TGFβRI, MUC16, and Thy-1 bind to MSLN (but not to each other), and SMAD7 binds to the complex. TGF-β1 exposure triggers the separation of Thy-1 and MUC16 from TGF-βri, promoting COL1A1 expression. In Msln-/ -APF, the absence of Msln increases the formation of the inhibitory Thy-1-TGFβRI complex and blocks the expression of COL1A1. Fgf-induced pathways differ, with impaired AKT phosphorylation, impaired compensatory ERK1/2 phosphorylation, and altered JAK2/STAT3 activation