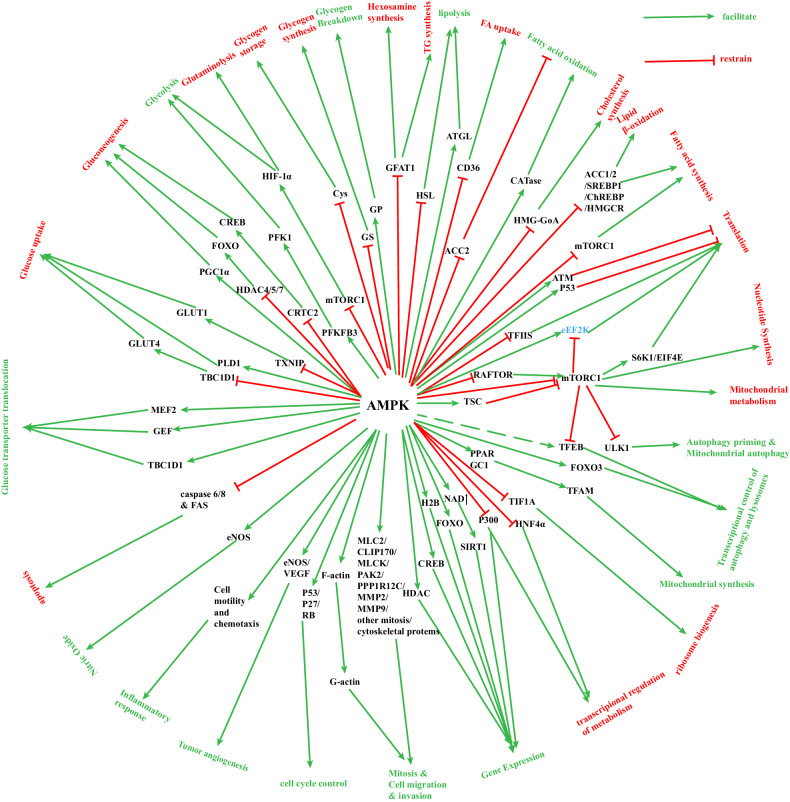
Fig. 3. The regulation of AMPK on energy metabolism, mitochondrial homeostasis, and autophagy.
AMPK activation regulates a variety of energy metabolic pathways. Green arrows represent up-regulated processes while red blockers represent down-regulated processes. Text in green font indicates biological processes that are mainly upregulated by AMPK, while text in red font indicates biological processes that are mainly downregulated by AMPK. These processes can be classified into glucose metabolism, lipid metabolism, protein metabolism, mitochondrial homeostasis, autophagy, and ribosome regulation. It is evident that AMPK plays a central role in energy metabolism and oxidative metabolism. AMPK AMP-activated protein kinase, GFAT1 Glutamine fructose-6-phosphate amidotransferase 1, HSL hormone-sensitive triglyceride lipase, ATGL adipose triglyceride lipase, CD36 Platelet glycoprotein 4, ACC2 acetyl-CoA carboxylase 2, mTORC1: mechanistic target of rapamycin complex1, ATM Ataxia Telangiectasia Mutated, P53 Cellular tumor antigen p53, eEF2K Eukaryotic extension factor 2 kinase, TSC TSC Complex Subunit 1, S6K1 Ribosomal S6 kinase 1, EIF4E eukaryotic initiation factor 4E, ULK1 Unc-51-like kinase, PPAR peroxisome proliferators-activated, GC1 Glume Coverage 1, TFAM Transcription Factor A, Mitochondrial, TIF1A Transcription Intermediary Factor 1-Alpha, HNF4α hepatocyte nuclear factor 4alpha, SIRT1 Silent Mating Type Information Regulation 2 Homolog 1, NAD nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide, H2B: histone 2 B, CREB: cyclic-AMP response binding protein, HDAC histone deacetylase, MLC2 Myosin Light Chain 2, VEGF vascular endothelial growth factor, eNOS endothelial nitric oxide synthase, FAS fatty acid synthesis, TBC1D1 Tre-2/BUB2/cdc 1 domain family 1, GEF GMP exchange factor, MEF2 myocyte enhancer factor-2, PLD1 Phospholipase D1, GLUT Glucose Transporter, TXNIP thioredoxin-interactingprotein, PFKFB3 6-Phosphofructo-2-Kinase/Fructose-2,6-Biphosphatase 3, PFK1 Phosphofructokinase-1, HIF-1α Transcription Intermediary Factor 1-Alpha, GS Glutamine synthetase, GP Glycogen phosphorylase.