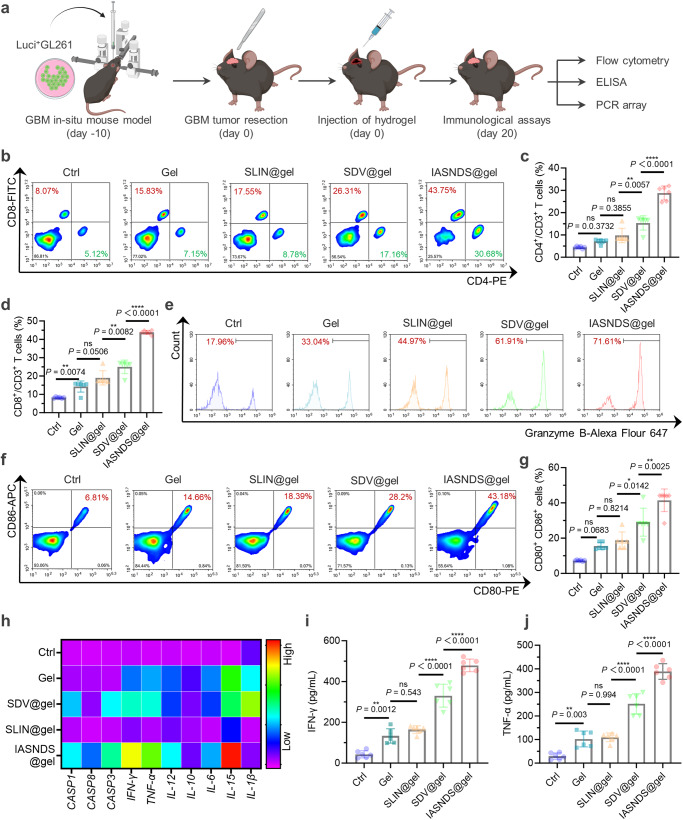
Fig. 7. Immunomodulatory efficacy of the Salmonella-loaded hydrogel system for mobilizing immunity against tumors via intracavity injection.
a Schematic of the experimental design for assessing immunomodulatory efficacy. b Flow cytometry results showing CD3+ cells in brain tissues after GBM removal in each treatment group. c Quantitative analysis of CD3+CD4+ cytotoxic T cells (n = 6 independent experiments). (exact P value: SDV@gel vs. IASNDS@gel P = 1.57104E-08); ****P < 0.0001. d Quantitative analysis of CD3+CD8+ cytotoxic T cells (n = 6 independent experiments). (exact P value: SDV@gel vs. IASNDS@gel P = 1.32267E−10); ****P < 0.0001. e Flow cytometry results indicating CD3+CD8+Granzyme B+ T cells in GBM tissues from different treatment groups. f, g Flow cytometry analysis and statistical analysis of CD80+CD86+ cells in GBM tissues after different treatments (n = 6 independent experiments). h Heatmap displaying the expression profiles of pyroptosis-related proteins, cytokines, and chemokines in brain tumor tissues. (n = 3 independent experiments). i, j Statistical analysis of IFN-γ expression and TNF-α expression in GBM tissues under different treatment conditions (n = 6 independent experiments). (exact P values of i: SLIN@gel vs. SDV@gel P = 1.22239E−07, SDV@gel vs. IASNDS@gel P = 8.7998E−07; exact P values of j: SLIN@gel vs. SDV@gel P = 2.02309E−07; SDV@gel vs. IASNDS@gel P = 3.4876E−07); ****P < 0.0001. Data are presented as the mean ± S.D. The statistical comparisons in c, d, g, i and j were performed using one-way ANOVA with Tukey’s post hoc test, with asterisks indicating significant differences (ns = no significance, *P < 0.05, **P < 0.01, ***P < 0.001, ****P < 0.0001). Source data are provided as a Source Data file.