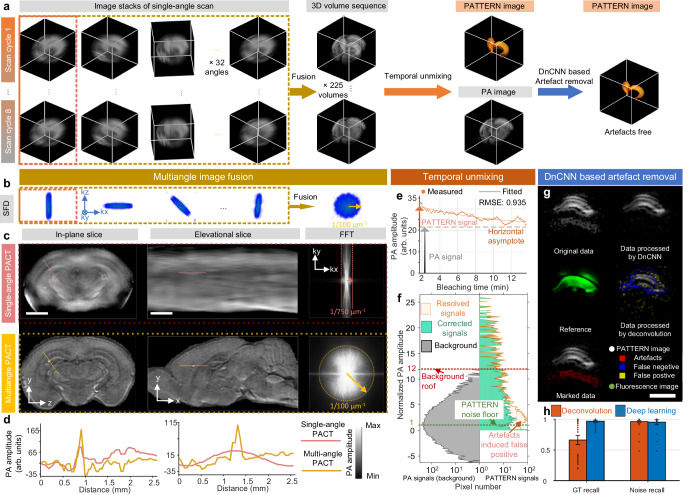
Fig. 2. PATTERN enables near isotropic and high-fidelity imaging of the whole brain and fluorescent tags.
a Data processing procedure of PATTERN. b SFD of each scan related to different angles in (a). c Resolution enhancement of the elevational direction by a rotation strategy. The first row, single angle scan reconstruction; the second row, multiangle scan reconstruction. The fast fourier transform (FFT) results indicate significant improvement, corresponding with (b). Scale bars, 2 mm. d Profiles of PA amplitude of lines indicated in (c). e Temporal unmixing results of the point related to the arrow in Fig. 1g. f Histograms of both PA signals (gray) and PATTERN signals (orange) in Fig. 1g; the corrected PATTERN signals guided by confocal are marked individually in green. Green dashed line, the noise floor is estimated as three times the standard deviation of PATTERN signals’ noise. Red dashed line, the roof of PA signals (maximum of background). g Diagram of the artifacts removal results using DnCNN with respect to the PATTERN signal of a hippocampus slice. Scale bar, 1 mm. h Comparison of ground truth (GT) recall and noise recall between the deconvolution-based method and deep learning method. n = 77 biologically independent image slices. Error bar length: 2 * standard error of the mean (SEM).