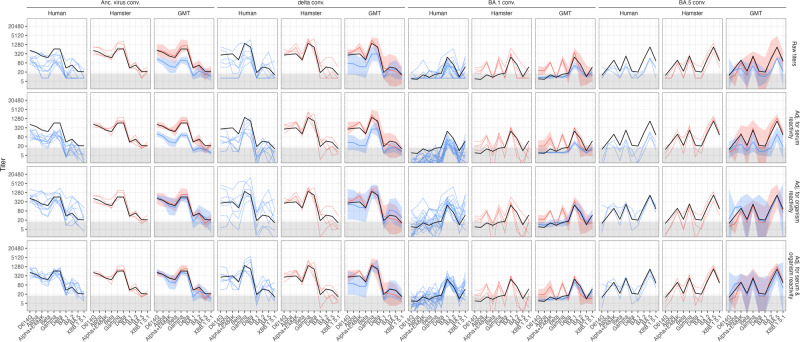
Fig. 1. Comparison of neutralization titers in hamster and human single variant exposure sera.
Human and hamster single variant exposure sera (human n = 10 ancestral, n = 7 delta, n = 17 BA.1, n = 3 BA.5; hamster n = 4 ancestral, n = 4 delta, n = 4 BA.1, n = 3 BA.5) were analyzed for neutralizing antibodies against D614G, alpha, alpha+E484K, beta, gamma, delta, BA.1, BA.2, BA.5, XBB.1.5.1 variants using a focus reduction assay and authentic virus variants. To control for titer variation due to different reactivities of individual sera and estimate species-specific effects, titers were estimated using a Bayesian framework (Supplementary Methods)5. The columns show human titers (blue), hamster titers (pink), and the GMT (geometric mean titers) ± +95% CI (confidence interval) as bold colored line and shaded area for each convalescent (conv.) serum group. The black line represents the estimated Geometric Mean Titer per serum group across organisms after adjusting for serum and organism effects. The rows show from top to bottom: Raw titers with titers <LOD (limit of detection ≤ 16 indicated by grey area) set to 8 (LOD/2), titers adjusted for individual serum reactivity variation, titers adjusted for organism reactivity differences, and titers adjusted for both individual serum and organism reactivities.