Figure 5. Acb2 antagonizes tri- and di-nucleotide based CBASS immunity.
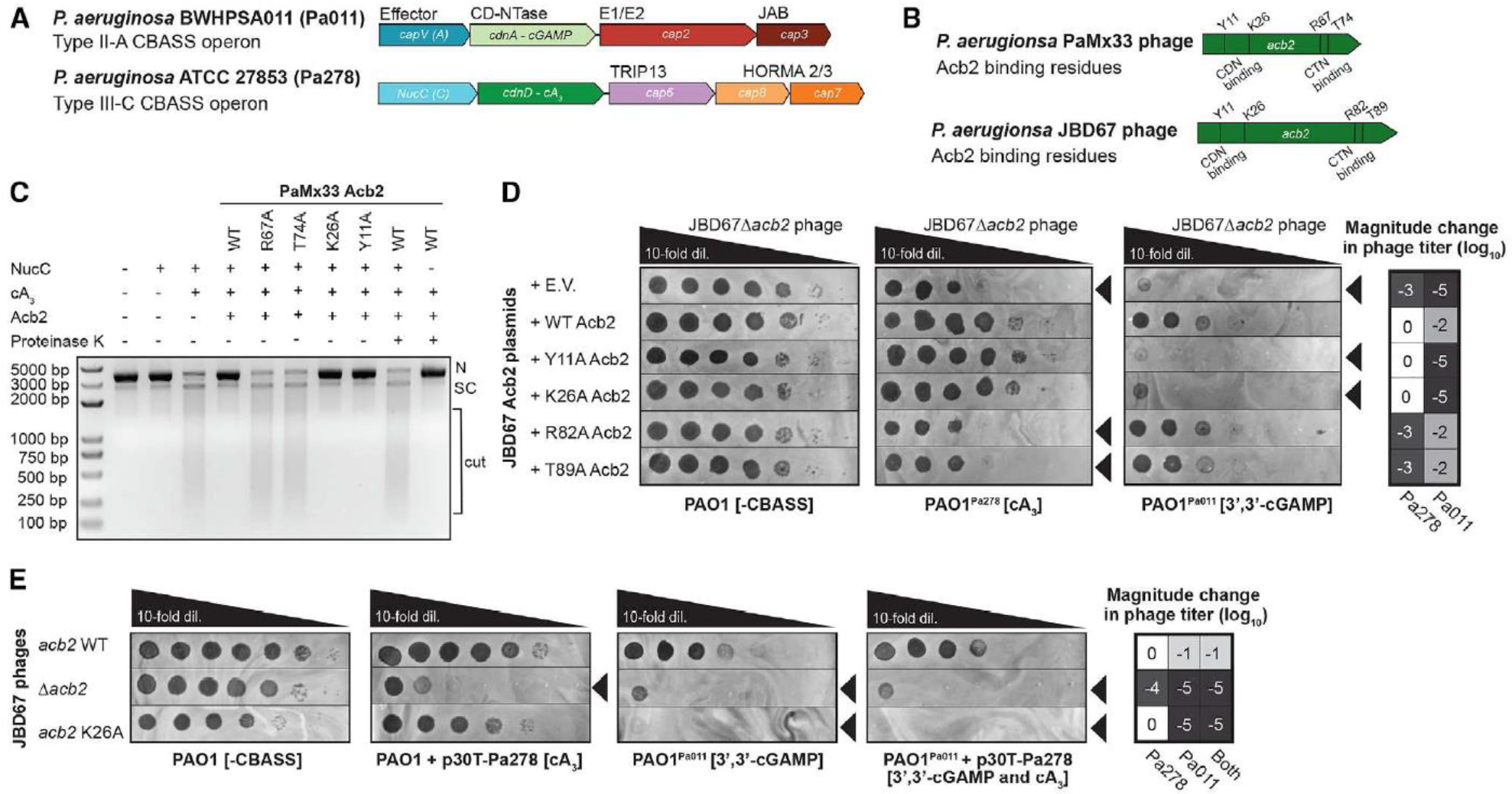
(A) Pseudomonas aeruginosa BWHPSA011 (Pa011) Type II-A CBASS and ATCC 27853 (Pa278) Type III-C CBASS operons.
(B) Pseudomonas aeruginosa PaMx33 and JBD67 phages acb2 gene annotated with residues essential for CDN (3’,3’-cGAMP) binding and CTN (cA3) binding.
(C) Effect of PaMx33 Acb2 or its mutants on cA3-activated NucC effector protein function. After treatment with proteinase K, the released cA3 also showed the ability to activate the nuclease activity of NucC. The concentration of NucC, cA3, Acb2 and proteinase K is 10 nM, 5 nM, 50 nM and 1 μM, respectively. N denotes nicked plasmid, SC denotes closed-circular supercoiled plasmid, and cut denotes fully digested DNA.
(D) Plaque assays with JBD67Δacb2 phage spotted in 10-fold serial dilutions on PAO1 strains harboring an empty vector (E.V.) plasmid or JBD67 Acb2 variants. The PAO1 strains either contain no CBASS operon (-CBASS), a chromosomally integrated Pa011 CBASS operon (PAO1Pa011), or a chromosomally integrated Pa278 CBASS operon (PAO1Pa278). These plaque assays were used to quantify the order of magnitude change in phage titer by comparing the number of spots (with plaques, or clearings if plaques were not visible) on the PAO1Pa011 or PAO1Pa278 CBASS-expressing strains divided by the PAO1 (-CBASS) strain (n=3). Basal expression of the Pa011 CBASS operon and 0.3mM IPTG-inducible expression of the Pa278 CBASS operon is sufficient for phage targeting. Black arrowheads highlight significant CBASS-dependent reductions in phage titer.
(E) Plaque assays with JBD67 phages spotted in 10-fold serial dilutions on PAO1 strains with and without CBASS. Pa278 CBASS was expressed from the pHERD30T (p30T) plasmid, while Pa011 CBASS was expressed from the chromosome. These plaque assays were used to quantify the order of magnitude change in phage titer (n=3). Basal expression (i.e. no arabinose added) of the Pa278 CBASS operon is sufficient for phage targeting. Black arrowheads highlight significant CBASS-dependent reductions in phage titer.
