Fig. 2. The E. coli divisome is built in stages.
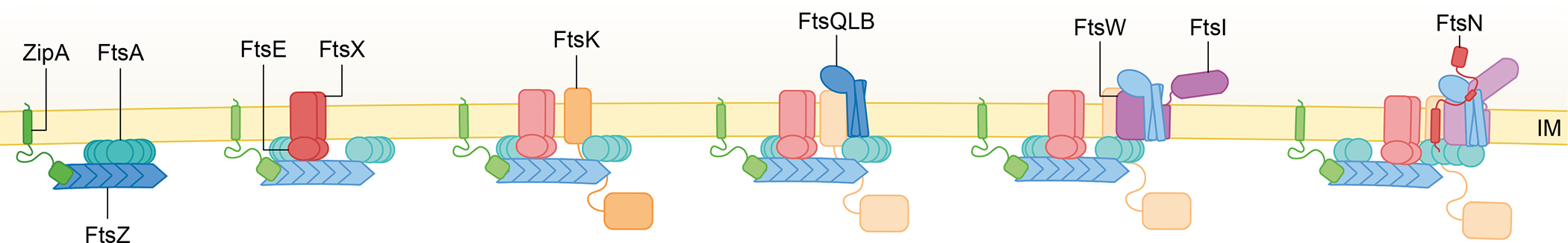
FtsZ is tethered to the membrane by FtsA and ZipA, forming the proto-ring. This is accompanied by the recruitment of the ABC transporter-like FtsEX complex and FtsK, which contains an N-terminal membrane bound domain required for cell division connected to a cytoplasmic DNA motor domain via a long linker. The next complex to be recruited is FtsQLB, which is important for recruitment and activation of the septum-specific transpeptidase (FtsI) and glycosyltransferase (FtsW). FtsN binds to and activates FtsWI enzymatic activity and is present at high concentrations at later stages. FtsN’s four distinct domains, the short cytoplasmic tail (FtsNcyto), transmembrane domain, essential periplasmic domain (FtsNE), and SPOR domain, are highlighted in the cartoon. The recruitment stage for each protein is highlighted by more intense coloring.
