Fig. 5. Binding of a small molecule inhibitor to the FtsZ interdomain cleft.
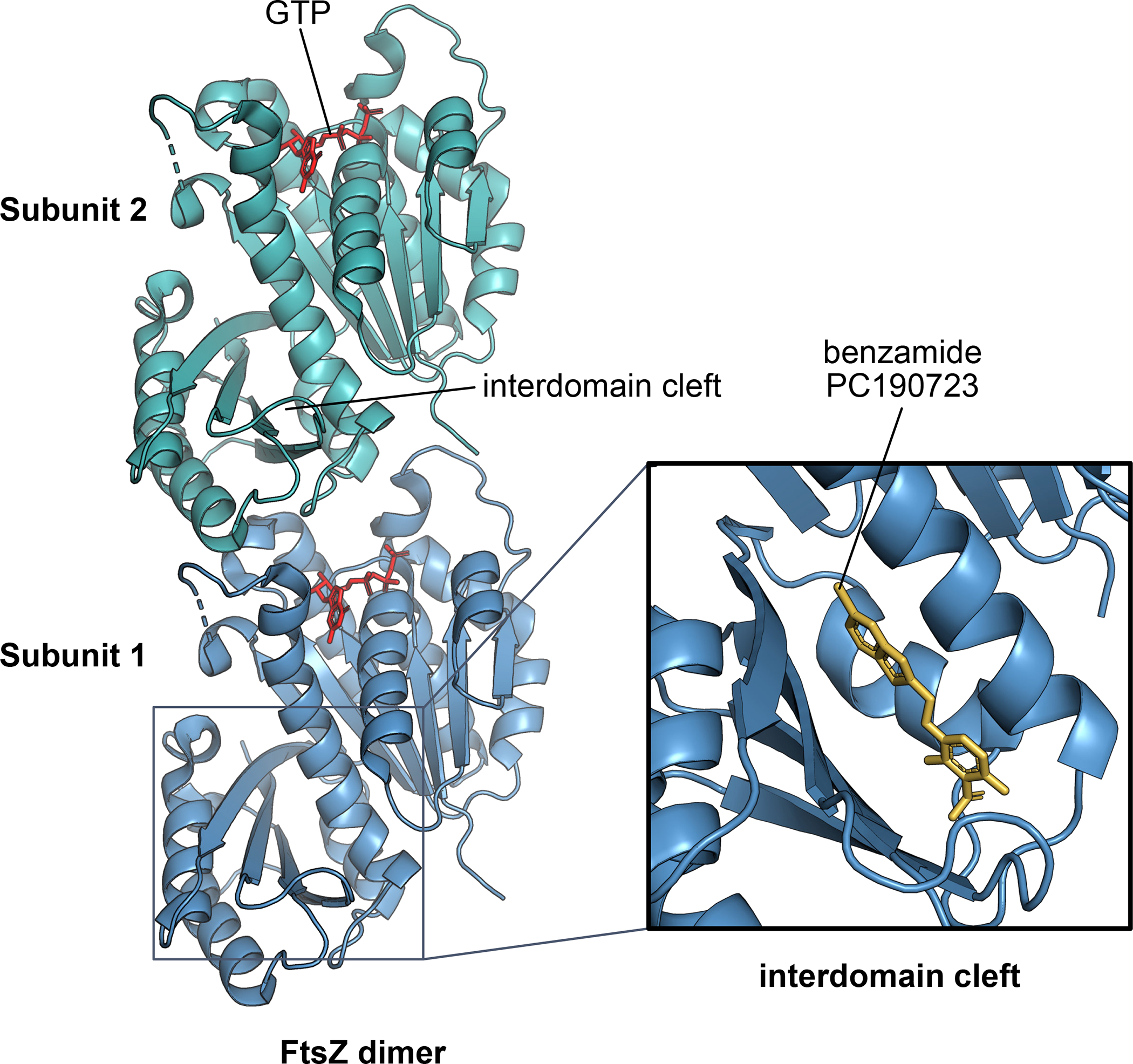
A dimer of the core polymerizing domain of FtsZ is shown, highlighting the interdomain cleft that connects the N-terminal GTP binding domain with the C-terminal domain. Many small molecule inhibitors of FtsZ, including the benzamide PC190723 and its derivatives, insert into the interdomain cleft (inset) and inhibit conformational changes within the FtsZ subunit required for its ability to dynamically treadmill.
