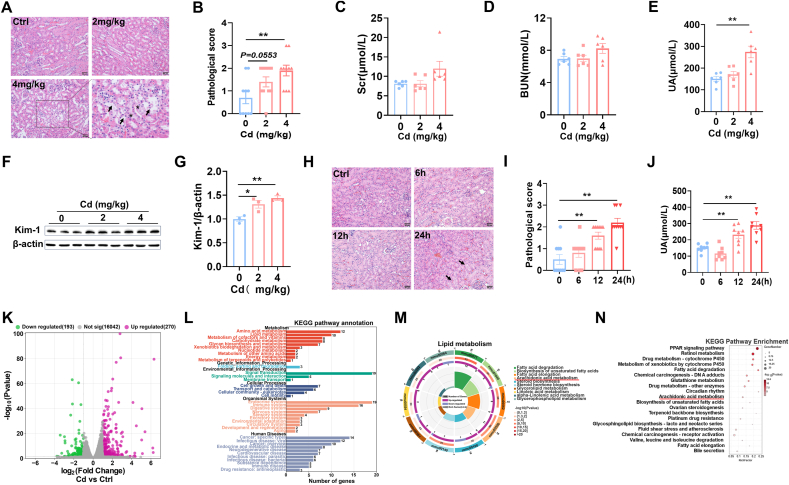
Fig. 1.
Acute Cd exposure induces acute kidney injury and changes in renal lipid metabolic pathway. CdCl2 (2 mg/kg or 4 mg/kg) was injected intraperitoneally into adult BALB/c male mice. Kidney tissues and blood sera were taken 24 h after CdCl2. (A and B) Renal pathology was assessed. (A) Representative H&E images. (B) Pathological score. (C) Scr. (D) BUN. (E) Serum UA. (F and G) Kim-1 was measured by immunoblot. (F) Representative images. (G) Kim-1/β-actin. CdCl2 was injected intraperitoneally into adult BALB/c male mice for 0, 6, 12 and 24 h (4 mg/kg), respectively. Kidney tissues and blood were taken 24 h after CdCl2. (H and I) Renal pathology was assessed. (H) Representative H&E images. (I) Pathological score. (J) Serum UA. (K–N) Transcriptome analyses were performed in Cd-exposed mice kidney. (K) Scatter plot. (L) The KEGG pathway enrichment was analyzed. (M) Lipid metabolic pathways were analyzed. (N) Top of KEGG pathway was enriched. All data are presented as mean ± S.E.M. (N = 6–8). *P < 0.05, **P < 0.01.