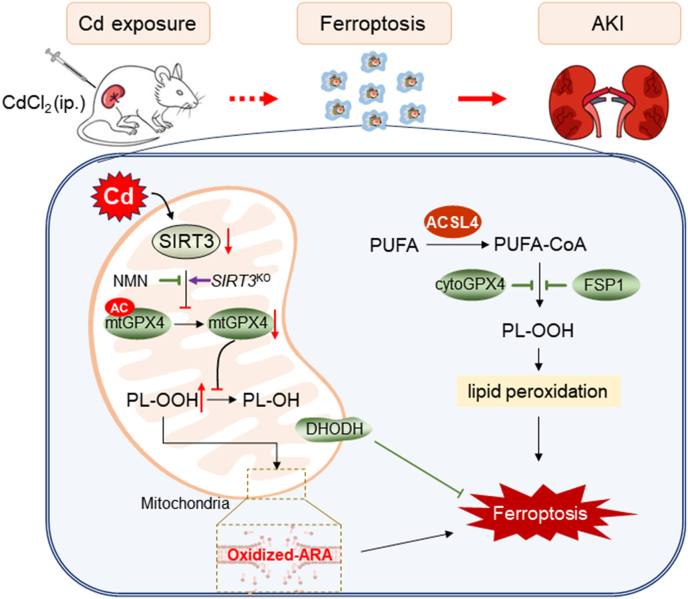
Fig. 8.
Role of mitochondrial GPX4 acetylation in Cd-induced renal cell ferroptosis and acute kidney injury. Briefly, acute Cd exposure reduces mitochondrial SIRT3, resulting in mitochondrial GPX4 acetylation and mitochondrial GPX4 reduction in mouse kidney. Mitochondrial GPX4 reduction induces elevation of mitochondrial oxidized lipids, mainly oxidized ARA, subsequently renal cell ferroptosis and acute kidney injury. Mitochondrial GPX4 acetylation, probably caused by SIRT3 reduction, is partially involved in Cd-induced renal cell ferroptosis. ACSL4: Acyl-CoA synthetase long chain family member 4; AKI: Acute kidney injury; ARA: arachidonic acid; CdCl2: Cadmium dichloride; DHODH: Dihydroorotate dehydrogenase; FSP1: Ferroptosis suppressor protein 1; GPX4: Glutathione peroxidase 4; NMN: Beta-Nicotinamide Mononucleotide; PUFA: Polyunsaturated fatty acids; SIRT3: Sirtuin 3.