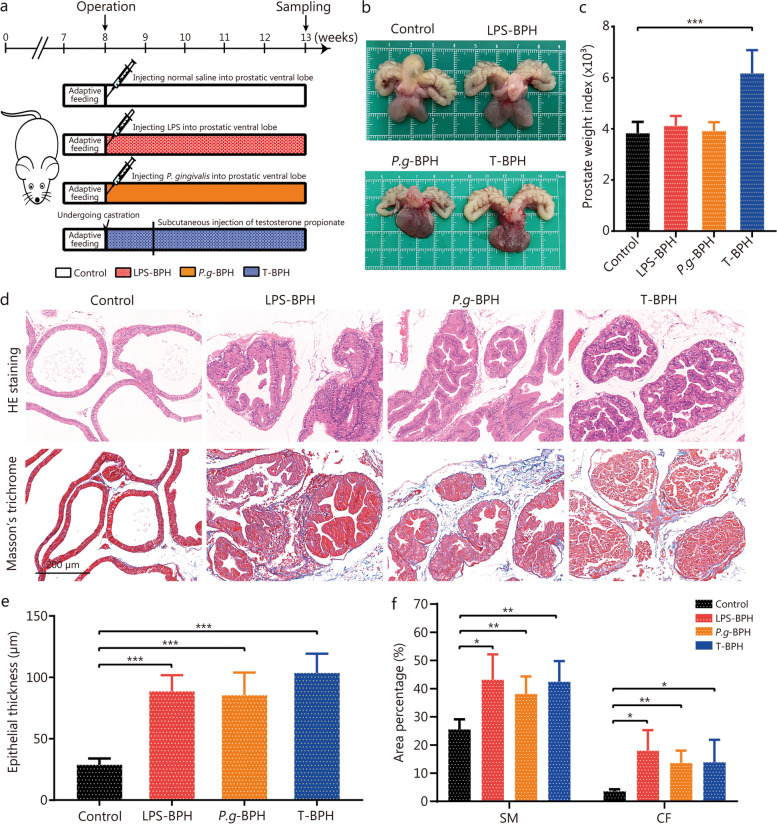
Fig. 3.
Transplantation of P. gingivalis induced BPH symptoms in rat prostate tissues. a Flowchart of P. gingivalis and P. gingivalis LPS infection rat model establishment. b Photographs of ventral prostate, bladder, and seminal vesicle from the control, P.g-BPH, LPS and T-BPH groups. c Histogram of prostate weight index (prostate weight of each animal/body weight of each animal) × 1000. d Representative figures from HE staining and Masson’s trichrome staining for the prostate tissues (original magnification ×200). e Bar graph for area percentage of epithelia from the groups. f Bar graph for area percentage of SM and CF from the groups. Data are expressed as mean ± SD. *P < 0.05, **P < 0.01, ***P < 0.001. LPS-BPH Porphyromonas gingivalis lipopolysaccharide induced BPH group, P.g-BPH Porphyromonas gingivalis induced BPH group, T-BPH Testosterone-induced BPH group, HE hematoxylin and eosin, SM smooth muscle, CF collagen fibers