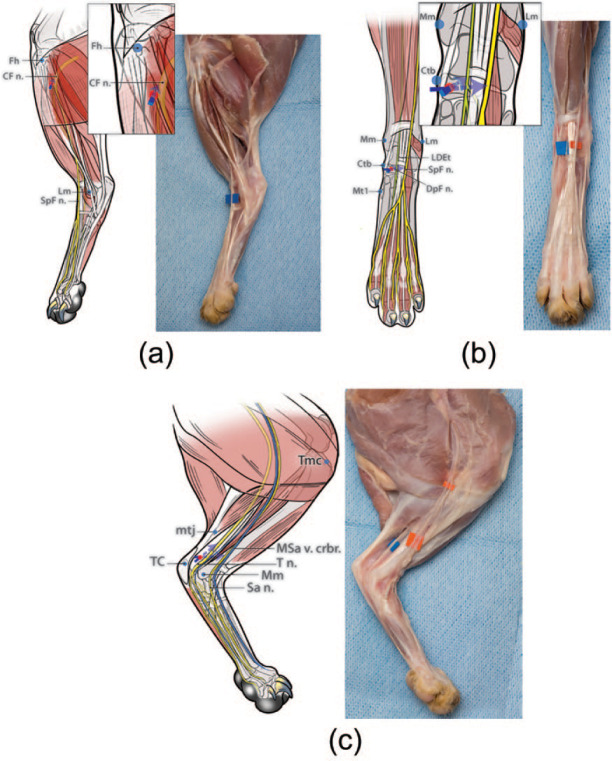
Figure 2.
Diagrams illustrating the developed and tested injection technique for each nerve. To perform the ‘distal crus block’ the common fibular nerve (CF n.), tibial nerve (T n.) and saphenous nerve (Sa n.) should be blocked. To perform the ‘distal pes block’ the superficial fibular nerve (SpF n.), deep fibular nerve (DpF n.), T n. and Sa n. should be blocked. (a) CF n. (for distal crus block): the fibular head (Fh) is readily identified by palpating the fibular shaft from a distal to proximal direction. The injection site is identified on the shaft of the fibula approximately 10 mm distal to the Fh (ie, about 10% of the distance from the Fh to the lateral malleolus [Lm]). A 25 G × 5/8 inch needle is gently inserted at this location, perpendicular to the lateral aspect of the limb until the tip of the needle contacted the shaft of the fibula, only a few mm deep to the skin. The needle is then withdrawn slightly and the injection performed (0.1 ml/kg). (b) SpF n. and DpF n. (for distal pes block): the injection target for the SpF n. and DpF n. is identified on a transverse plane level with the palpable medial surface of the central tarsal bone (Ctb) (ie, approximately at the midpoint between the medial malleolus of the tibia [Mm] and the base of the first metatarsal bone [Mt 1]) and approximately 9 mm from the medial surface of the Ctb towards the limb axis (ie, immediately adjacent to the palpable long digital extensor tendon [LDEt]). A 25 G × 5/8 inch needle is passed subcutaneously, medially to laterally, inserted at the medial surface of the Ctb, and with the bevel facing upwards. The needle is advanced until its tip is located superficial to the dorsal surface of the LDEt and then the injection is performed (0.05 ml/kg). Then, the needle is withdrawn a few mm and redirected deeply in the same transverse plane towards the medial edge of the LDEt (ie, from a dorsomedial direction) to block the DpF n. The needle is advanced a few mm until its tip is located deep to the medial edge of LDEt and then the injection is performed (0.05 ml/kg). (c) T n. and Sa n. (for distal crus block and distal pes block): the injection site for the T n. is identified at approximately 30 mm proximal to the medial surface of the tuber calcanei (TC) (ie, at the musculotendinous junction [mtj] of the common calcanean tendon) and 7 mm cranial to the mtj (ie, in the fossa bound cranially by the distal caudal surface of the tibia and caudally by the mtj of the common calcanean tendon). A 25 G × 5/8 inch needle, with the bevel facing up, is inserted medially, subcutaneously from a distal to proximal direction in the fossa until the tip of the needle is at the same level as the mtj of the common calcanean tendon. Then the injection is performed (0.05 ml/kg). To block the Sa n. using the same needle insertion point, the needle is redirected cranially towards the tibia (ie, towards the medial saphenous vein cranial branch [MSa v. crbr.] passing over the medial shaft of the tibia). The needle is advanced until its tip is located over the center of the tibial shaft and then the injection is performed (0.05 ml/kg). Red dots indicate the site of needle insertion. The blue arrows represent the direction of needle insertion to reach the desired injection site