Extended Data Figure 10 |. A traveling-direction signal computed via optic flow is robust to changes in the yaw angle of the fly’s head.
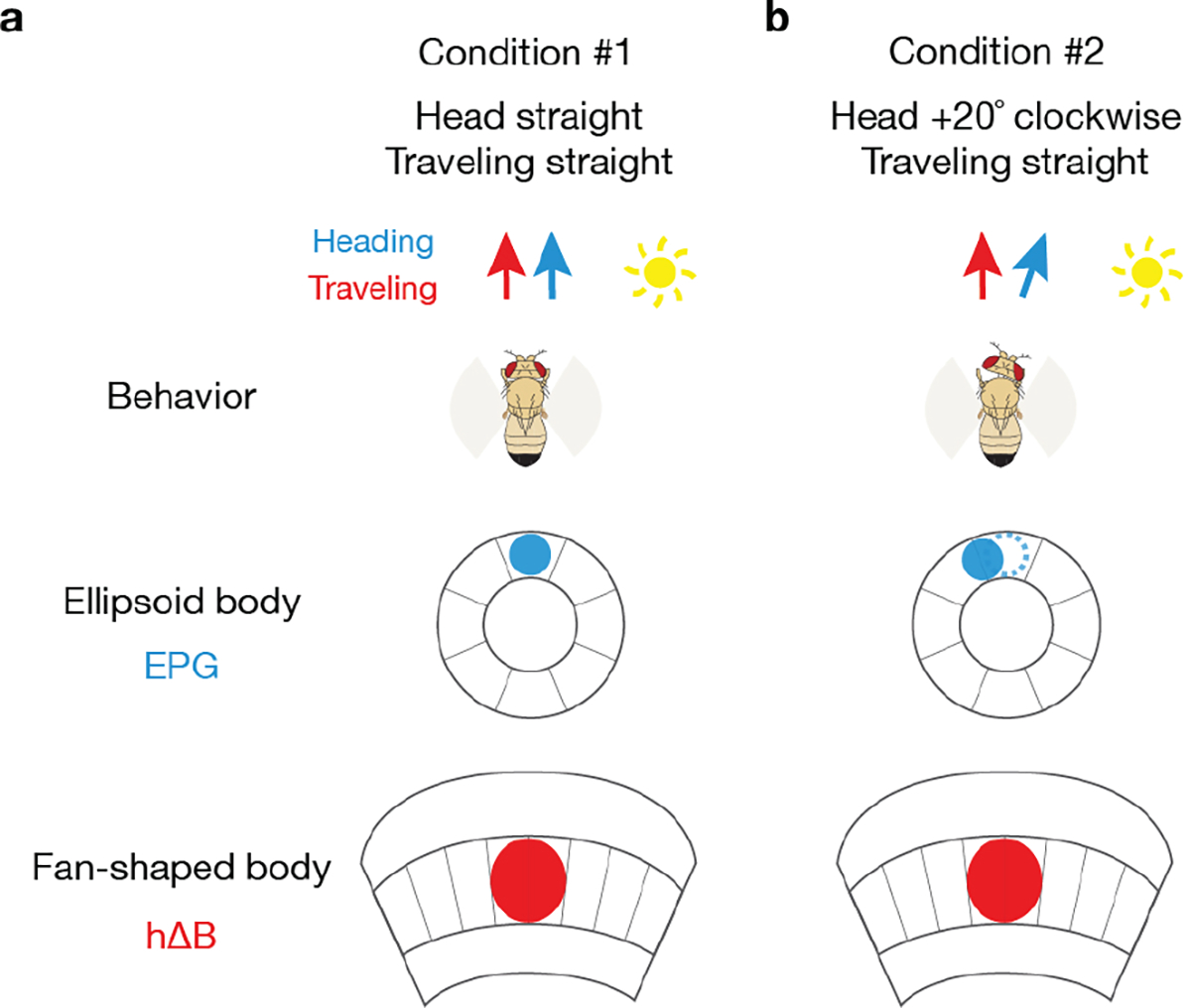
a, Fly flying straight with the head aligned to the body axis. EPG and hΔB signals are aligned in the ellipsoid body and fan-shaped body, respectively. b, Fly flying straight forward with the head rotated 20° to the right. The EPG bump––assuming the EPG bump position tracks the fly’s head (rather than body) direction––will rotate 20° counterclockwise. The hΔB bump, however, will remain pointing in the same allocentric traveling direction because the net effect of the EPG bump rotating 20° in one direction and the ego-motion signal from optic flow (not represented in the diagram) rotating 20° in the opposite direction is that the PFR/hΔB bump stably indicates the same traveling direction throughout.
