Figure 2 |. The allocentric traveling direction can be computed by vector rotation and summation, which can be implemented by phasors.
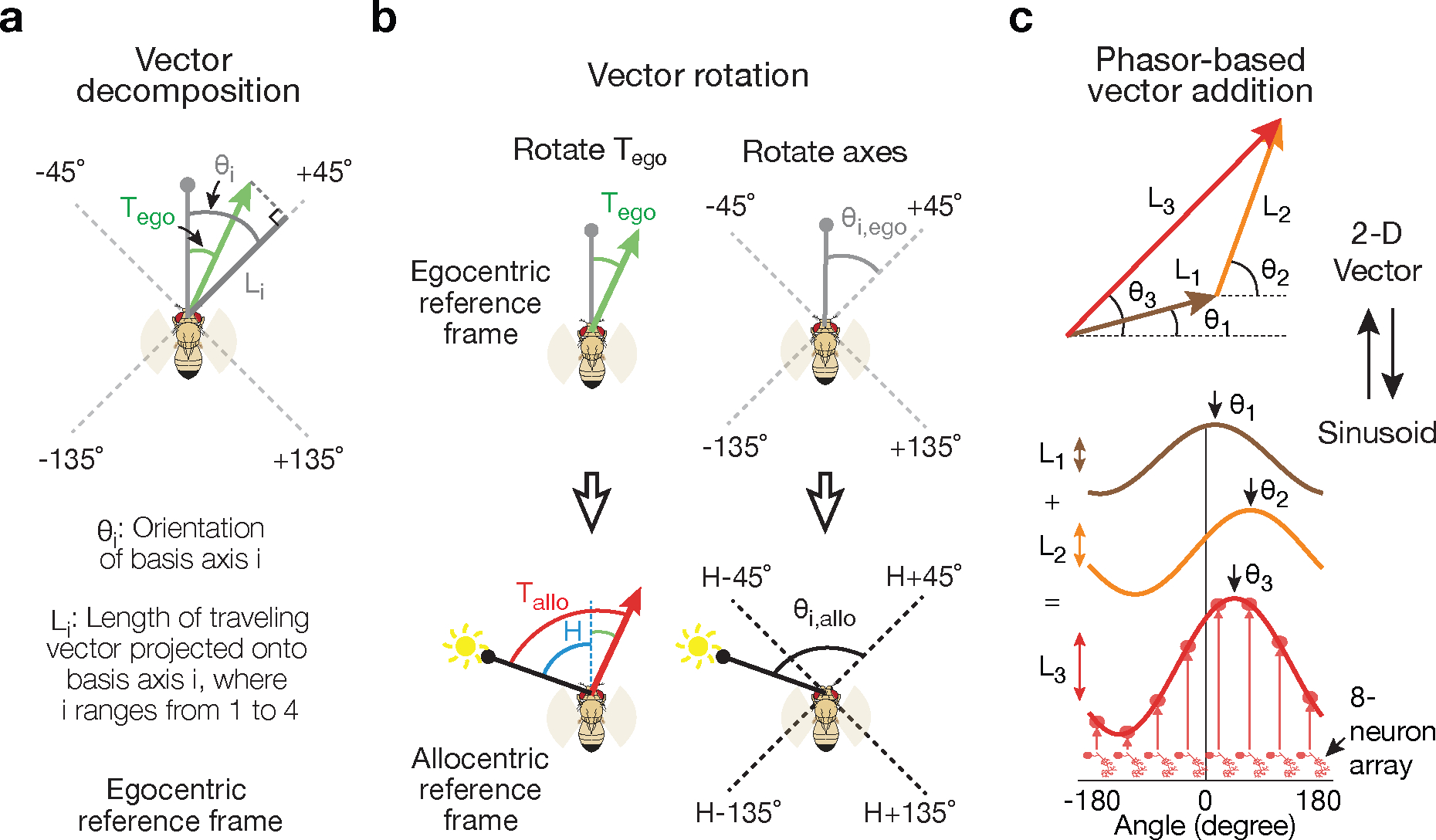
a, The traveling-direction vector (green) for a fly translating at an egocentric traveling angle Tego, referenced to its head direction (gray line with circle), is projected onto four axes oriented ±45° and ±135° relative to the head, yielding four scalars L1–4. The +45° projection is shown. The fly’s head direction represents 0° in this egocentric reference frame. Angles are positive clockwise. b, The fly’s allocentric traveling direction, Tallo, can be computed either by rotating the egocentric traveling angle (Tego) such that it becomes referenced to the external world (i.e., the sun) (top) or, as in the fly circuit, by first referencing the ±45° and ±135° projection axes to the external world (bottom) and then taking the vector sum of the four projection vectors. Egocentric vectors are referenced to the external world by adding H, the fly’s allocentric heading angle, to them. c, Two-dimensional vectors can be represented by sinusoids and adding sinusoids then implements vector addition.
