Extended Data Fig. 4 |. Mechanical, scanning, and optical modifications to increase 3P signal and decrease average power.
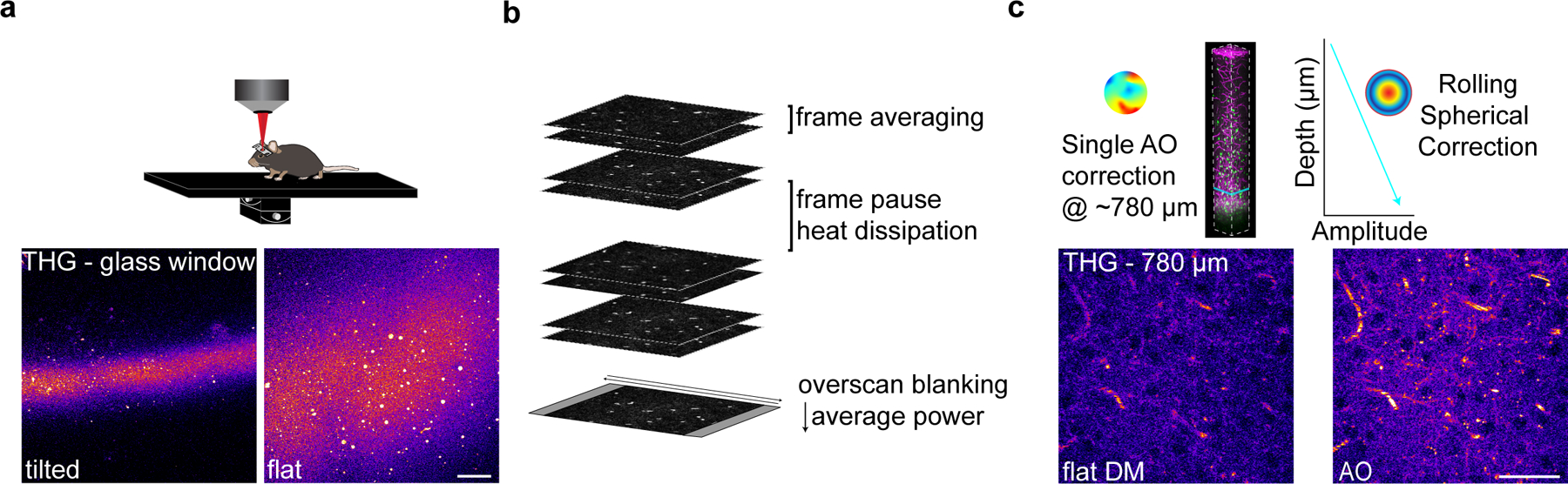
a) The third harmonic generation (THG) signal at the surface of the cranial window was used to align the preparation orthogonally to the excitation light. b) Scanning modifications to increase SBR and decrease average power to mitigate risk of tissue damage. Frame averaging was advantageous compared to increasing the pixel dwell time to reduce risk of nonlinear damage. Z-stack acquisition was paused periodically to allow for heat dissipation (1 min. pause per 3 min. scanning). Laser pulses were blanked on the galvanometer overscan to reduce the average power applied to the preparation at each z-plane. c) Imaged-based AO correction increased SBR at depth (left) and modulating the spherical aberration correction linearly with depth improved SBR throughout the imaging volume (right). For longitudinal imaging, the AO correction was made before acquiring each time point at the same z-plane just above the scattering white matter (750–850 μm depth).
