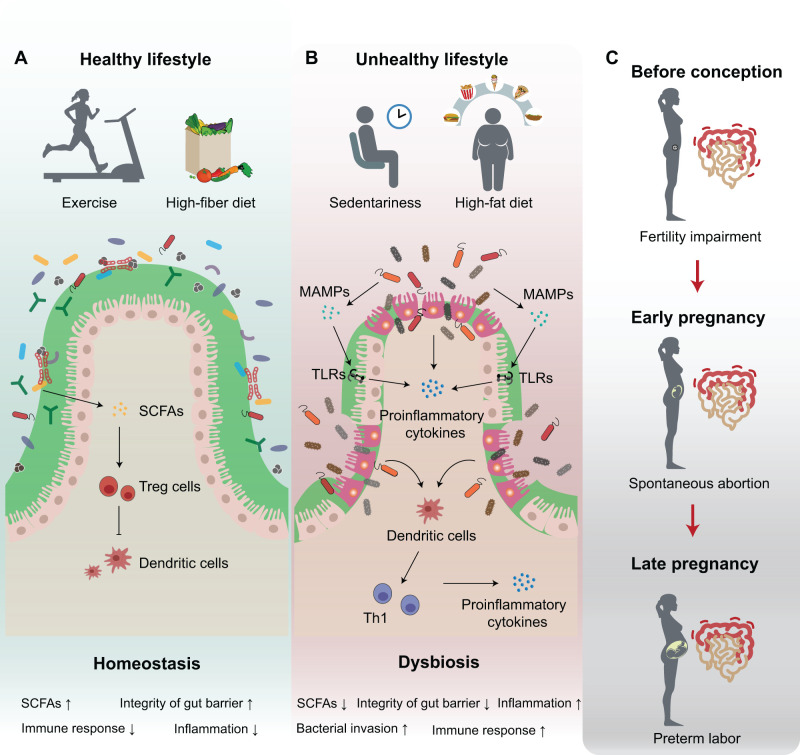
Figure 1.
Lifestyle influences gut microbiome and is associated with reproductive healthA. The impact of healthy lifestyle on gut microbiome and immunity. Active lifestyles such as regular exercise and a high-fiber diet can balance the gut microbiome homeostasis, maintain the gut barrier integrity, and increase the production of SCFAs, which reduce the production of proinflammatory cytokines and down-regulate immune responses and thereby help maintain reproductive health. B. The impact of unhealthy lifestyle on the gut microbiome and immunity. Unhealthy lifestyles such as sedentariness and a high-fat diet disrupt the gut microbiome, which further impairs the gut barrier integrity. The evasion of pathogens stimulates immune cells to produce more proinflammatory cytokines, which subsequently activates the immune responses and potentially induces various diseases related to reproductive health. C. Persistent inflammation in the intestine at different gestational stages may induce adverse pregnancy outcomes such as fertility impairment, spontaneous abortion, and preterm labor. MAMP, microbe-associated molecular pattern; SCFA, short-chain fatty acid; Th1, T helper type 1; Treg, regulatory T; TLR, Toll-like receptor.