Fig. 1. Human NK cells mediate antigen-specific responses against HIV and influenza.
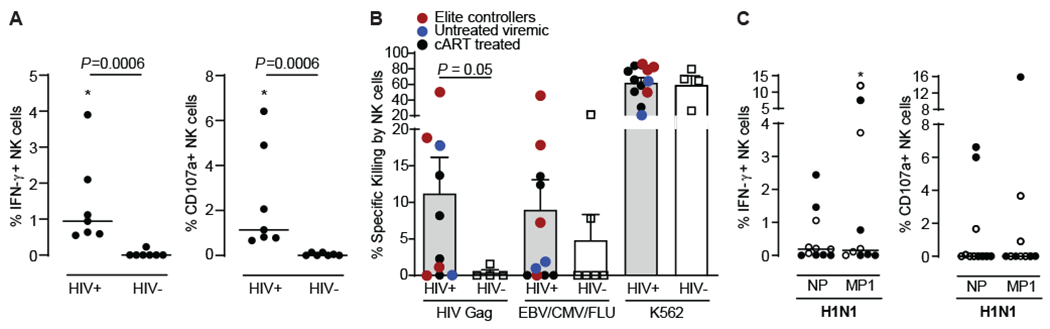
(A) Enriched NK cells from PLWH (N=7) or healthy donors (N=7) were co-cultured with autologous BLCL that had been pulsed with 2ug/mL peptide pools derived from HIV Gag (HIV-1 Consensus B; provided by the NIH AIDS Reagent Program) and NK cell responses assessed by ICS. Dead cells were excluded. Dot plots show proportions of IFN-γ+ and CD107a+ NK cells after subtracting background (unstimulated). (B) Autologous BLCL were pulsed with a pool of HIV Gag overlapping peptides or with the CEF (CMV, EBV and influenza) control peptide pool and were labeled with the CellTrace Violet dye. Mock-pulsed BLCL serving as intra-well controls were labeled with the green dye CFSE. Purified NK cells from PLWH (N=12) or healthy donors (N=6) were co-cultured with BLCL at 5:1 E:T ratios (equal mixture of pulsed target BLCL and unpulsed control BLCL) for 16 hours, and specific lysis of BLCL was determined by flow cytometry. Killing of HLA-deficient K562 cells was used as additional positive control. (C) Enriched NK cells from 11 HIV-negative healthy donors were incubated overnight with 2ug/mL peptide pools derived from influenza A/California/04/2009(H1N1) NP and A/California/08/2009(H1N1) MP1 and NK cell responses assessed by ICS. Dead cells were excluded. Dot plots show proportions of IFN-γ+ and CD107a+ NK cells after subtracting background (unstimulated). Full circle, positive for IgG antibodies against influenza A by ELISA. Empty circle, not tested for the presence of IgG antibodies against influenza A. Asterisks, significant differences compared to unstimulated controls. Data are represented as median and individual data points (A and C) or mean ± SEM and individual data points (B). Statistical significance was tested using Mann-Whitney U test for comparisons between PLWH (HIV+) and HIV-negative donors (HIV-) (A and B), or Wilcoxon signed-rank test for comparisons between unstimulated and stimulated NK cells (C). * p<0.05.
