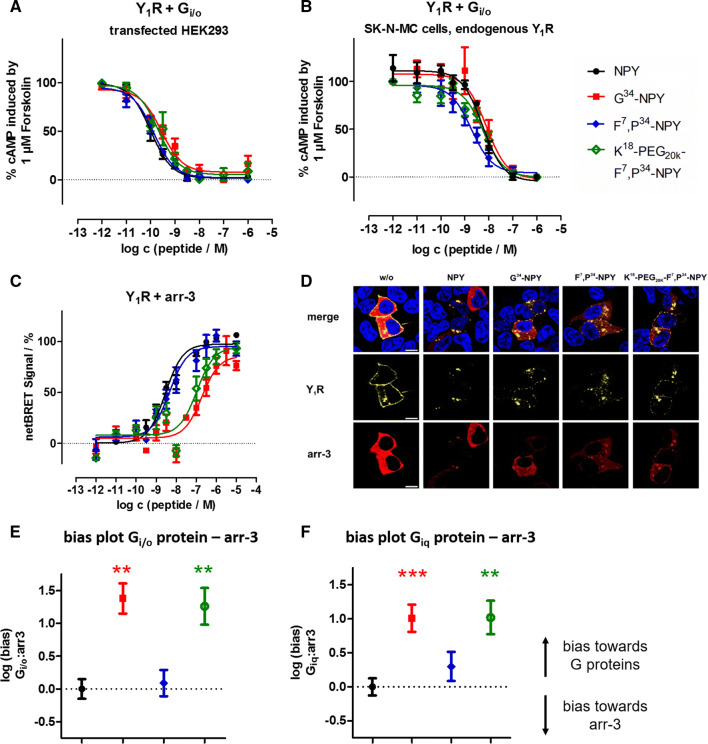
Fig. 3.
Novel Y1R agonists display impaired arr-3 recruitment and receptor internalization, leading to a net bias towards the G protein pathway. a, b CRE reporter gene assay to determine the activity of the peptides at the Y1R in the endogenous Gi/o pathway in transiently transfected HEK293 (a) and SK-N-MC cells endogenously expressing the Y1R (b). c BRET experiments with Y1R fused to eYFP and RLuc8-arr-3 in transiently transfected HEK293 cells. Cells were stimulated with peptide variants for 5 min. d Internalization and arr-3 recruitment was detected by fluorescence microscopy prior to (w/o) and after stimulation with 100 nM of Y1R ligands. Y1R is C-terminally fused to eYFP (yellow) and arr-3 is C-terminally tagged with mCherry (red). Nuclei were stained with Hoechst33342 (blue), n ≥ 2. (scale bar = 10 µm). e, f Ligand bias plot generated from arr-3 recruitment versus G protein activation downstream of the native Gi/o or chimeric Giq pathway in transfected HEK293 cells (cf. Table 1). Shown are the mean between-pathway differences (ΔΔlogEC50 ± SEM), and the statistical significance was tested by one-way ANOVA and Dunnett’s post test compared to NPY, **p < 0.01, ***p < 0.001