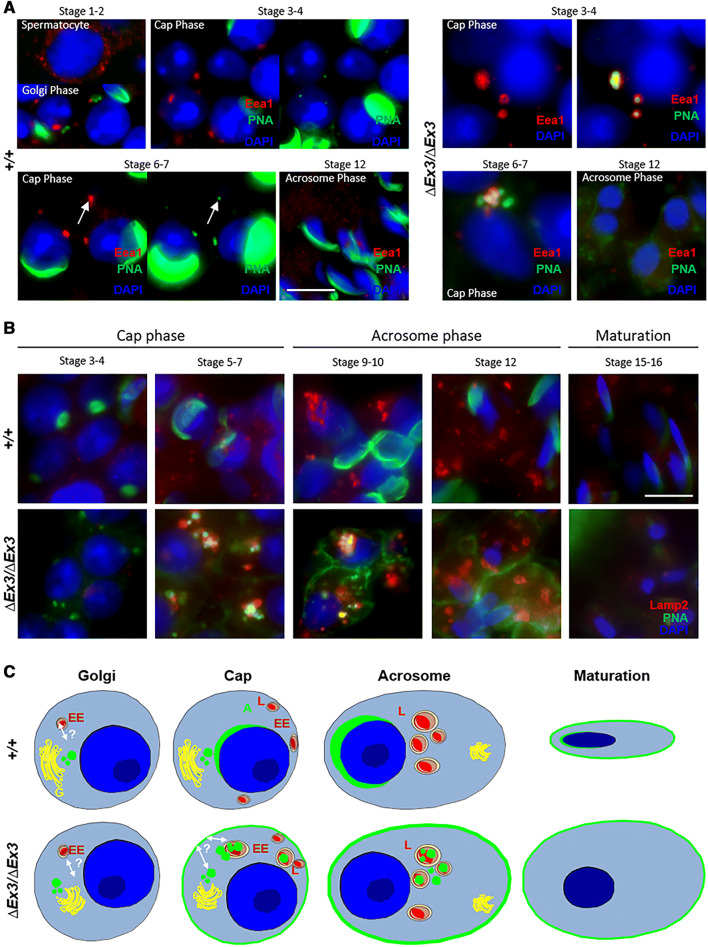
Fig. 7.
Proacrosomal vesicles are targeted to the endosome and lysosome in Vps13b∆Ex3/∆Ex3 spermatids. a Representative images of wild-type and mutant spermatids stained using anti-Eea1 antibody and PNA-FITC. PNA-positive vesicles scattered within mutant spermatids were frequently Eea1-positive. During cap phase, Eea1 signal in wild-type spermatids systematically colocalized with a small and faint PNA signal, while it was associated with larger and multiple vesicular structures in mutant spermatids. Left panels of cap phase wild-type spermatids were over-exposed to distinguish PNA signal at the endosomal structure. Images of cap phase mutant spermatids did not require over exposition to detect PNA signal at this structure. Scale bar 10 µm. b Representative images of wild-type and mutant spermatids stained using anti-Lamp2 antibody and PNA-FITC. In cap phase, mutant spermatids displayed larger Lamp2-positive structures than wild-type spermatids. In addition, PNA signal at and around these structures was prominently detected in mutant but not wild-type spermatids. Scale bar 10 µm. c Schematic representation of PNA-binding vesicle trafficking in developing mutant spermatids compared to the wild-type situation. In green is depicted the location of PNA-binding proteins. A acrosome, EE early endosome, G golgi, L lysosome