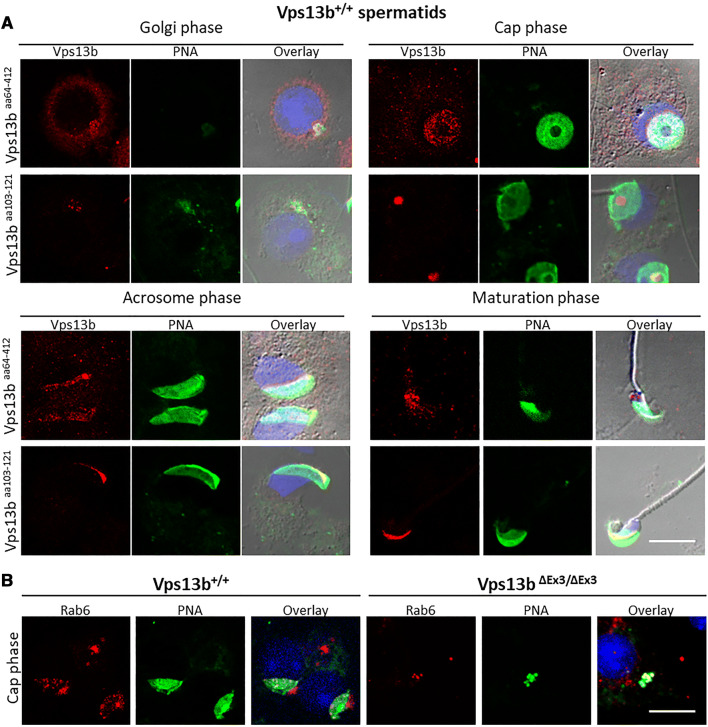
Fig. 8.
Vps13b and Rab6 locate to the acrosome. a Representative images of isolated wild-type spermatids in Golgi, cap, acrosome, and maturation phases stained against an epitope of Vps13b within amino acids 64–412 (upper panels) and an epitope at the C-terminus end of the Vps13b Chorein domain (amino acids 103–121, lower panels) and counterstained with PNA-FITC and DAPI. Overlay images include a DIC picture. Using both antibodies, results showed that Vps13b expression was not detectable at the Golgi apparatus of spermatogonia and spermatocytes. Expression of Vps13b increased in early spermatids. The protein essentially localized to proacrosomal vesicles in Golgi phase and to the acrosomal inner membrane (aa64–412) and acrosomal granule (aa103–121) in acrosome phase. Signals detected with Vps13baa64–412 gradually left the acrosome through maturation phase, while signals detected with Vps13baa103–121 remained at the acrosome. b Images of Rab6 staining on cap phase wild-type and mutant spermatids. Rab6 located to the Golgi apparatus of all spermatogenic cells. In addition, Rab6 followed the sequential acrosomal localization displayed by the Vps13b epitope comprised between amino acids 64 and 412 in wild-type spermatids. In mutant spermatids, it mainly remained at the Golgi apparatus and was sometimes found in mislocalized PNA-positive vesicles during cap phase. Scale bars 10 µm