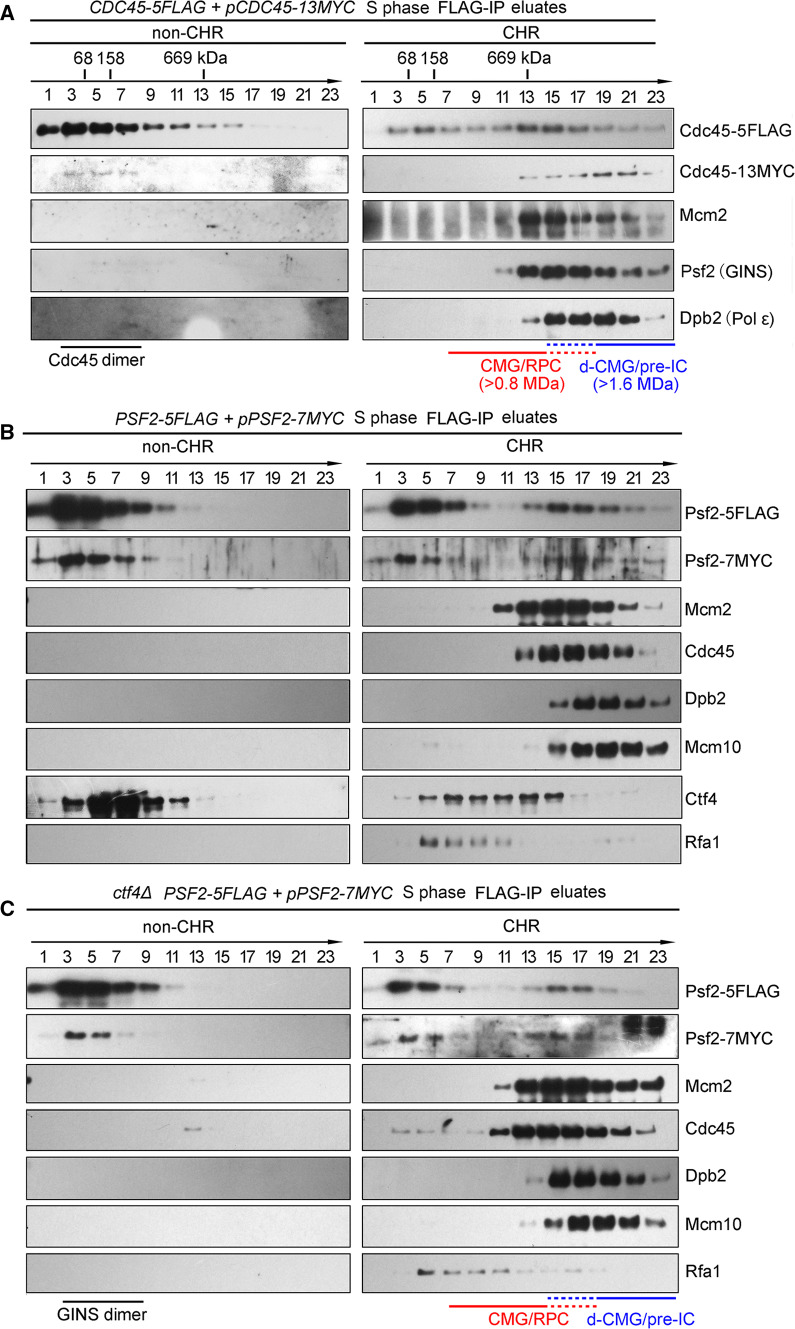
Fig. 4.
Formation of d-CMG is independent on Ctf4. a Glycerol density gradient separation of the Cdc45-containing complexes. The CDC45-5FLAG/pCDC45-13MYC (LL85-1, Table S1) cells were cultured and released into S phase for 40 min at 25 °C after α-factor synchronization. Cells were then collected and fractionated. The Cdc45-containing complexes were purified by subjecting the Cdc45-5FLAG eluates of non-CHR and CHR fractions to centrifugation on a 10–30% glycerol density gradient as described in Fig. 2. The species of CMG-containing complexes obtained in different fractions are indicated. The dashed lines represent the overlapping fractions of d-CMG and CMG. The sedimenting positions of protein standards are labeled. b, c Glycerol density gradient separation of the GINS-containing complexes. WT (LL67-1, Table S1) (b) or ctf4Δ (LL149-1, Table S1) (c) cells in the PSF2-5FLAG/pPSF2-7MYC background were collected and fractionated basically as above. The GINS-containing complexes were purified and analyzed similarly