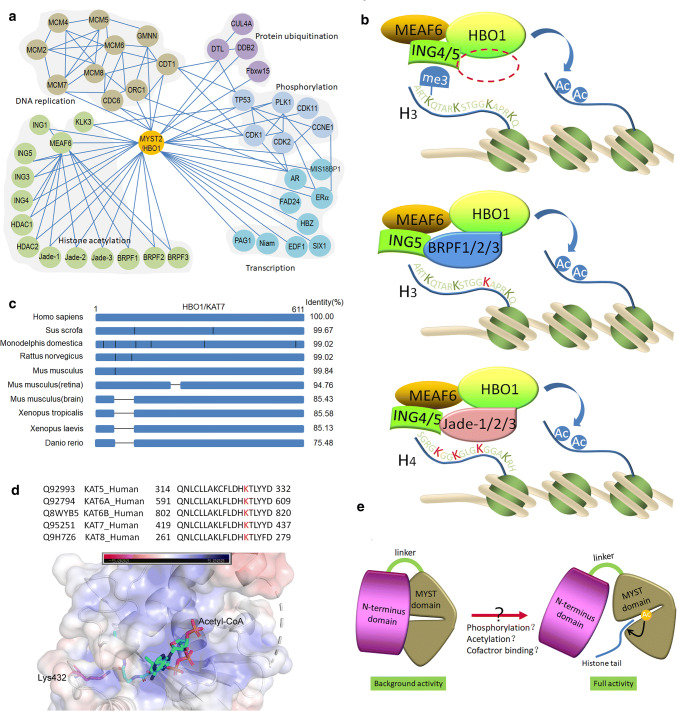
Fig. 3.
Regulation of HBO1 acetyltransferase activity. a References based protein–protein interaction networks of HBO1 with its cofactors and partner proteins. b HBO1 forms complexes with MEAF6, ING4, ING5 or BRPF1, BRPF2, BRPF3 or Jade-1, Jade-2, Jade-3, for binding to and acetylation histone H3 or H4. JADE1/2/3 directs acetylation toward the H4 tail (K5, K8 and K12), whereas BRPF1/2/3 targets H3 acetylation (K14). c Schematic diagram presented the sequence alignment of HBO1 among species. The vertical lines represent residue variants between the species. HBO1 is a conserved and widely expressed lysine acetyltransferase. However, there is a deletion (from 55 to 110 a.a.) in xenopus, zebrafish or partial tissues of mouse (brain/central nervous system or retina) in the N-terminus of HBO1. Interestingly, this sequence does not match any known motifs but consists of serine/threonine residues in rich abundance that may serve as phosphorylation sites for kinases such as CDKs and PLK1. d Lys432 is a conserved site in the MYST domain shared by MYST protein family located near the binding site of acetyl-CoA. It is autoacetylation and may regulate acetyltransferase activity and protein stability. e A proposed model suggests that NTD provides a regulatory switch for HBO1 activity. HBO1 includes two separate domains, the NTD (N-terminal domain) and MYST domain connecting by a hinge region. The close interaction of NTD with MYST domain rigidifies the full activation of HBO1 complexes, whereas conformation changes induced by modifications such as phosphorylation and acetylation, or binding of cofactor and substrate release MYST domain from the inhibition of NTD and subsequently switch the full activity of HBO1