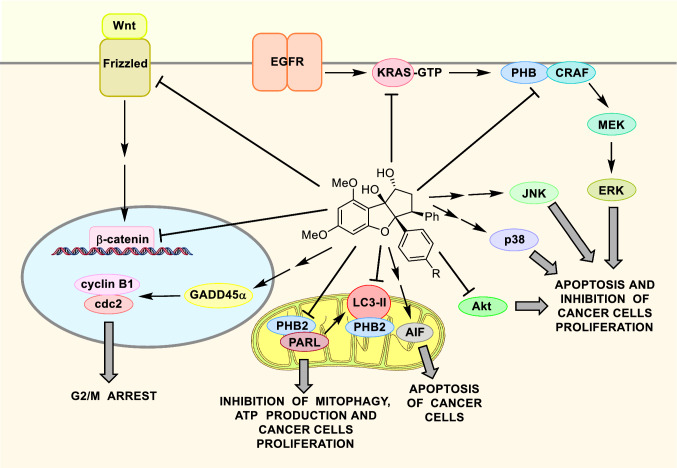
Fig. 4.
Overview of the mechanism of action of flavaglines in cancer cells involving PHBs. Flavaglines inhibit the activation of KRAS and C-RAF, to block the C-RAF/MEK/ERK pathway necessary to the survival of many cancer cell types. In bladder cancer, flavaglines inhibit PHB1 phosphorylation by Akt, leading to the removal of PHB1 in mitochondria. Flavagline also upregulate GADD45α to inhibit cdc2/cyclin B1 kinases and cell cycle progression in the G2/M phase. They can also inhibit the signaling of the paracrine factor Wnt that is necessary to the survival of several cancer cell types. Moreover, flavaglines block mitophagy and energy productions by inhibiting the effects of PHB2 on the mitochondrial inner protease PARL and LC3-II. Flavaglines can also induce apoptosis of cancer cells by activating AIF, JNK, p38 through yet uncharacterized mechanisms. Although it is critical to the cytotoxicity of flavaglines in cancer cells, the action of flavaglines on the initiation factor eIF4A is not disclosed to remain in the scope of this review