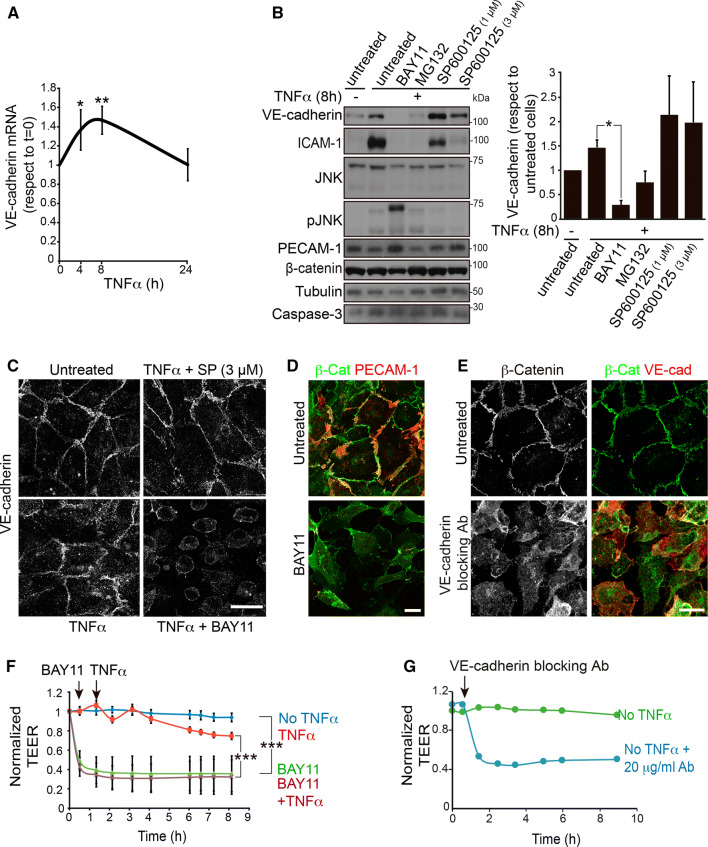
Fig. 4.
NF-κB is necessary for VE-cadherin expression and endothelial barrier function. a TNFα increases VE-cadherin mRNA levels. RT-qPCR of VE-cadherin mRNA from HUVECs stimulated with TNFα for the indicated times. Graph shows the mean + SEM from three independent experiments performed with two pairs of oligonucleotides. *p < 0.05; **p < 0.01. b The NF-κB inhibitors BAY11 (10 μM) and MG132 (20 μM), but not the JNK inhibitor SP600125, abrogate the expression of VE-cadherin and ICAM-1 (positive control) but not of β-catenin, PECAM-1, tubulin and caspase-3 in HUVECs. Graph shows the mean + SEM from three independent experiments. *p < 0.05. c Decrease of VE-cadherin expression in the presence of the NF-κB inhibitor BAY11 detected by immunofluorescence with a specific antibody. Scale bar, 20 μm. d Effect of Bay11 on endothelial cell morphology detected with anti-β-catenin and anti-PECAM-1 antibodies. Scale bar, 20 μm. e Effect of 20 μg/ml anti-VE-cadherin blocking antibody on endothelial adherens junctions detected with anti-β-catenin antibody. f The NF-κB inhibitor BAY11 induces endothelial barrier collapse. HUVECs were cultured at confluence for 48 h on ECIS electrodes pre-coated with fibronectin, starved for 12 h and then stimulated or not with 10 ng/ml TNFα in the presence or absence of 10 μm BAY11. Graphs show the mean + SEM from at least three independent TEER experiments. ***p < 0.001. g Blocking VE-cadherin with a specific antibody has the same effect than BAY11 on endothelial TEER levels