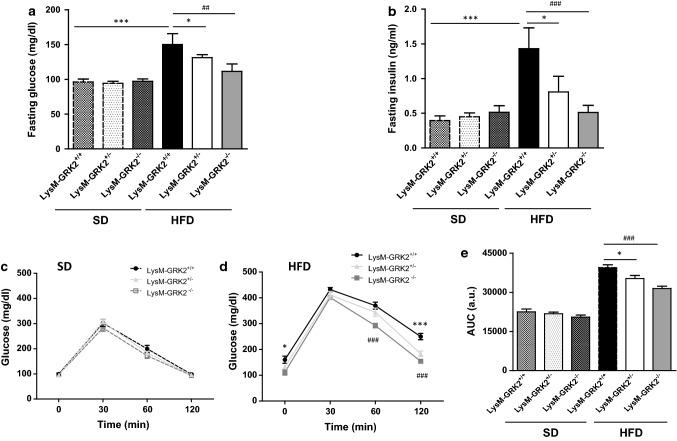
Fig. 1.
Decreasing GRK2 levels in myeloid cells protects against the development of HFD-induced glucose intolerance. 8-week old male mice from the LysM-GRK2+/+, LysM-GRK2+/− or LysM-GRK2−/− genotypes were either maintained on a SD or fed a HFD for 12 weeks. At the end of this period, serum glucose (a) and insulin (b) levels were measured upon an overnight fasting (~ 12 h). Intraperitoneal GTTs in the SD-fed (c) and the HFD-fed (d) groups were performed. e Histogram showing the GTTs area under the curve (AUC) analysis. Results are means ± SEM of 5–8 animals per group. Statistical analysis was performed by one-way (a and b) or two-way (e) ANOVA or by two-way repeated measures ANOVA (c and d) followed by Bonferroni’s post-hoc test. (*p < 0.05; **p < 0.01; ***p < 0.005 and ##p < 0.01; ###p < 0.005 for LysM-GRK2+/+ vs LysM-GRK2−/− comparison)