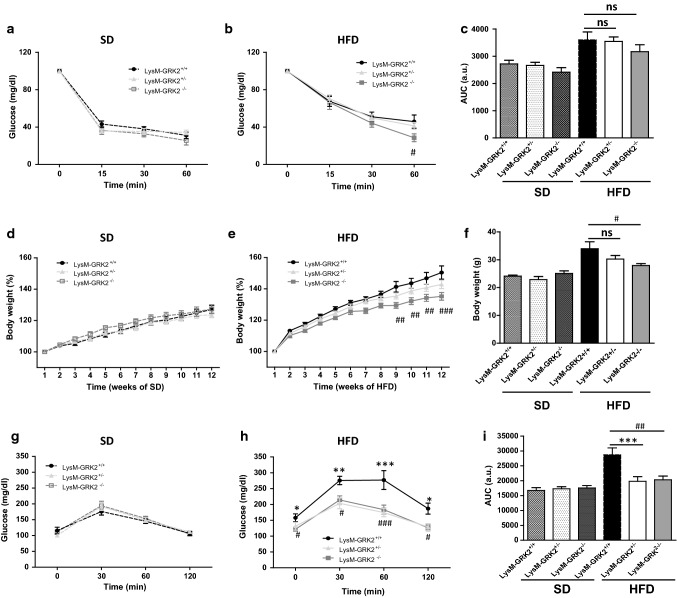
Fig. 2.
Decreasing GRK2 levels in myeloid cells does not cause important differences in systemic insulin sensitivity or body weight gain, but significantly improves pyruvate tolerance in HFD-fed mice. 8-week old male mice from the LysM-GRK2+/+, LysM-GRK2+/− or LysM-GRK2−/− genotypes were either maintained on a SD or fed a HFD for 12 weeks. Intraperitoneal ITTs in the SD-fed a and the HFD-fed b groups were performed. c Histogram showing the ITTs AUC analysis. Body weight evolution (expressed in %) during the 12 weeks of standard (d) or high fat (e) feeding, and final body weight at the end of the 12 weeks are shown (f). Intraperitoneal pyruvate tolerance tests (PTTs) in the SD-fed (g) and the HFD-fed (h) groups were performed. i Histogram showing the PTTs AUC analysis. Results are means ± SEM of 5–8 animals per group. Statistical analysis was performed by two-way repeated measures ANOVA followed by Bonferroni’s post-hoc test. (*p < 0.05; **p < 0.01; ***p < 0.005 and #p < 0.05; ##p < 0.01; ###p < 0.005 for LysM-GRK2+/+ vs LysM-GRK2−/− comparison)