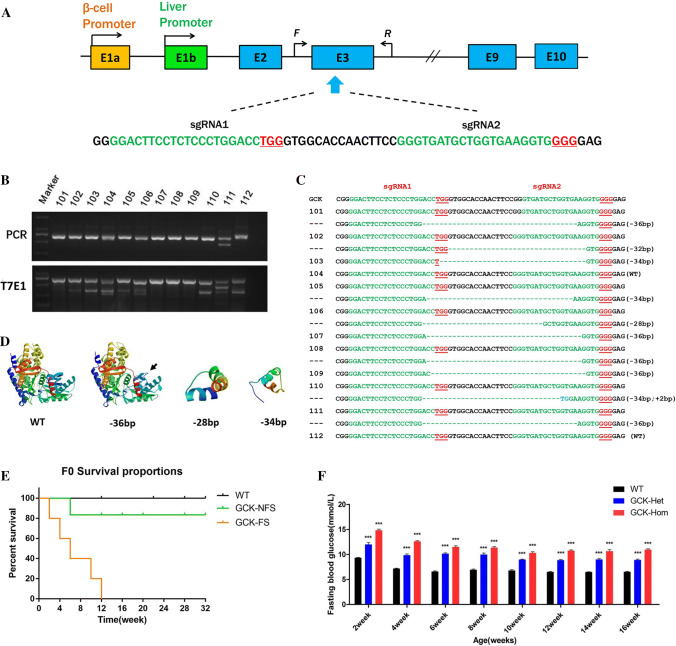
Fig. 1.
Genome editing of the GCK gene via the Cas9/gRNA system. a Schematic diagram of the 2 sgRNA target sites at the GCK gene locus. The CDS region is indicated by blue rectangles. sgRNA target sites are indicated by green. PAM sites are underlined and highlighted in red. F and R represent the PCR primer pairs used for mutation detection. b Mutation detection of F0 GCK-NFS rabbits by T7E1 cleavage assay. PCR products of the targeted GCK exon 3 region from 12 F0 rabbits (101–112) (upper panel) and their cleavage products (lower panel) are shown. c Genomic DNA sequences of the targeted region of GCK from the F0 rabbits 101–112, determined by sequencing the cloned PCR products. PAM sites are underlined and highlighted in red; target sequences are green; deletions (−) are shown. WT wild type. d Computer modeling 3D structure of GCK and its fragments. e Survival curves of wild type (WT), non-frame shift mutant (GCK-NFS) and frame shift mutant (GCK-FS) rabbits. f Fasting blood glucose levels of GCK-NFS rabbits are shown at the age from 2 to 16 weeks. The data were expressed as the mean ± SEM. A probability of p < 0.05 was considered statistically significant. *, p < 0.05; **, p < 0.01; ***, p < 0.005. ns not significant