Fig. 1.
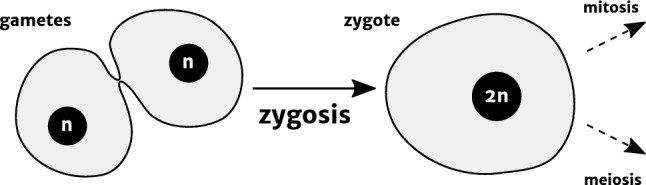
The rudiments of zygosis. Zygosis involves the fusion of two gametes (shown here immediately after the initial fusion of their membranes), followed by nuclear fusion of their nuclei to form a zygote, a new individual with twice the original genetic content (2n). Zygotes can either enter the mitotic cell cycle (in diplontic and haplo-diplontic organisms) or progress immediately to meiosis to regenerate haploid progeny (in haplontic organisms). Typically, but not always, gametes are monoploid and zygotes diploid
