Figure 5.
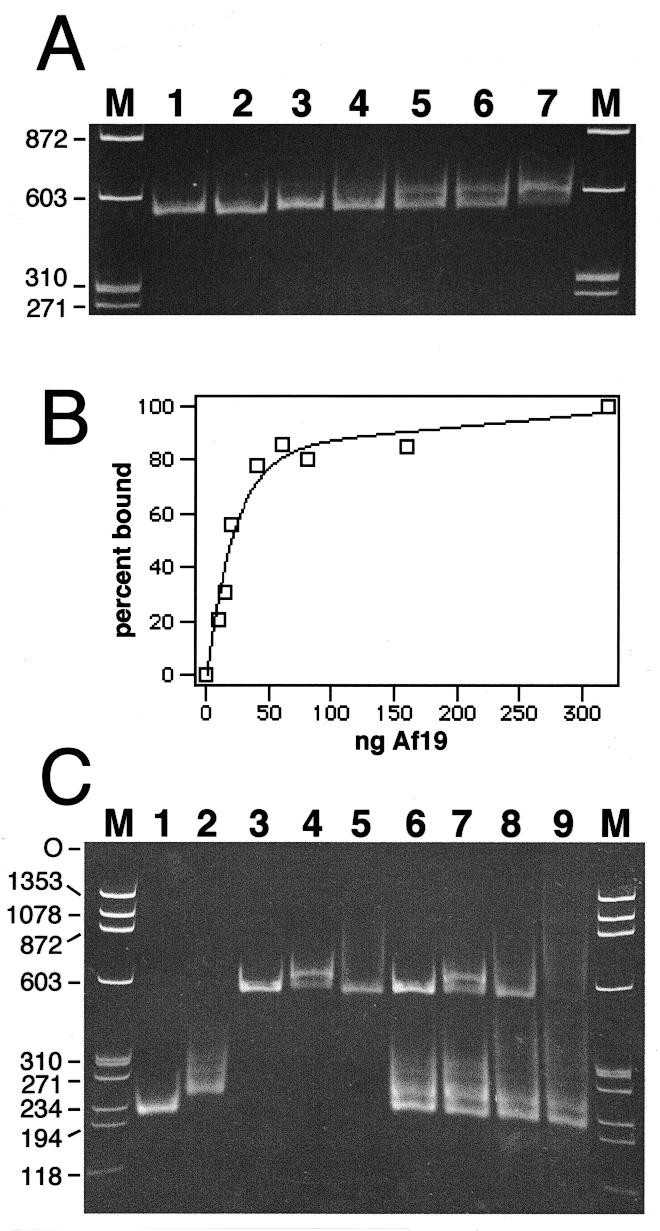
Formation of A.fulgidus SRP by mobility shift. Electrophoresis of SRP RNA–protein complexes on 6% native polyacrylamide gels. The nucleic acids were stained with ethidium bromide. (A) Binding of purified Af-SRP19 to Af-SRP RNA. Each reaction contained 200 ng RNA. Protein was added at RNA/protein molar ratios of 0.082 (lane 2), 0.21 (lane 3), 0.41 (lane 4), 0.61 (lane 5), 0.82 (lane 6) and 1.6 (lane 7). The sizes of double-stranded DNA fragments (HaeIII-digested ΦX174 DNA) used for reference (lanes M) are indicated in base pairs on the left. (B) Quantitative analysis of Af-SRP19 binding to Af-SRP RNA by mobility shift as shown in (A). (C) Binding of Af-SRP19 and Af-SRP54 to various SRP RNAs. Lane 1, 200 ng Δ35-SRP RNA of M.jannaschii (Mj-Δ35); lane 2, 200 ng human Δ35-SRP RNA (h-Δ35); lane 3, 200 ng full-length A.fulgidus SRP RNA (Af-SRP); lane 4, 200 ng Af-SRP with 60 ng Af-SRP19 protein; lane 5, 200 ng Af-SRP with 700 ng Af-SRP54; lane 6, mixture of Mj-Δ35, h-Δ35 and Af-SRP RNA with amounts identical to those used in lanes 1–3; lane 7, RNA mixture as in lane 6 with the addition of 60 ng Af-SRP19; lane 8, RNA mixture as in lane 6 with the addition of 700 ng Af-SRP54; lane 9, RNA mixture as in lane 6 with addition of 60 ng Af-SRP19 and 700 ng Af-SRP54. Sizes of double-stranded DNA fragments used for reference (lanes M) are indicated in base pairs on the left.
