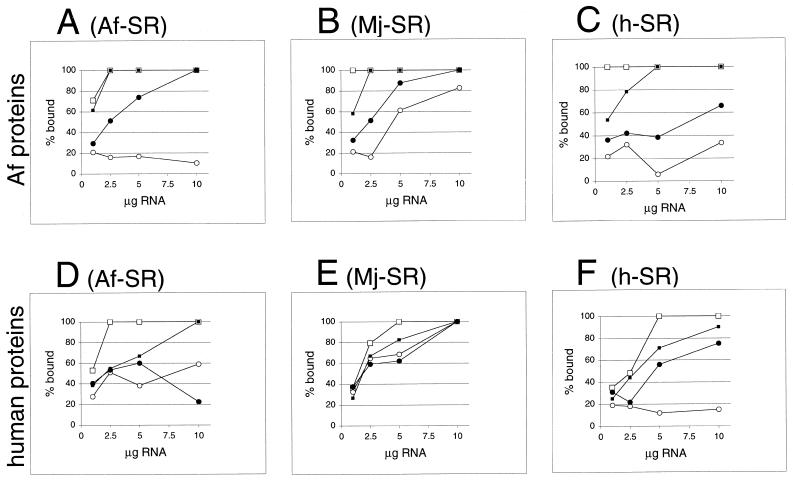
Figure 7.
Formation of ribonucleoprotein particles with A.fulgidus, M.jannaschii or human SRP RNAs. Activity of A.fulgidus SRP proteins (A–C) or human SRP proteins (D–F) with variable amounts of SRP RNAs of A.fulgidus (A) and (D), M.jannaschii (B) and (E) or H.sapiens (C) and (F) measured in the DEAE affinity assays (see Materials and Methods) from the intensity of Coomassie blue-stained polypeptides separated by SDS–PAGE as shown in Figure 6. Binding of SRP19 proteins is indicated by lines connected to open squares; open circles mark binding of Af-SRP54 (A–C) or human SRP54M (D–F). Solid squares indicate binding of SRP19 in presence of Af-SRP54 or human SRP54M; solid circles show binding of Af-SRP54 or human SRP54M in presence of SRP19. Small amounts of background binding observed without RNA or in presence of tRNA in the range of 3–10% observed with Af-SRP54 or human SRP54M (see Results) were plotted. Equimolar protein concentrations were 1 µg Af-SRP19, 3.8 µg Af-SRP54, 1.3 µg human SRP19 and 2 µg human SRP54M per 50 µl reaction volume.