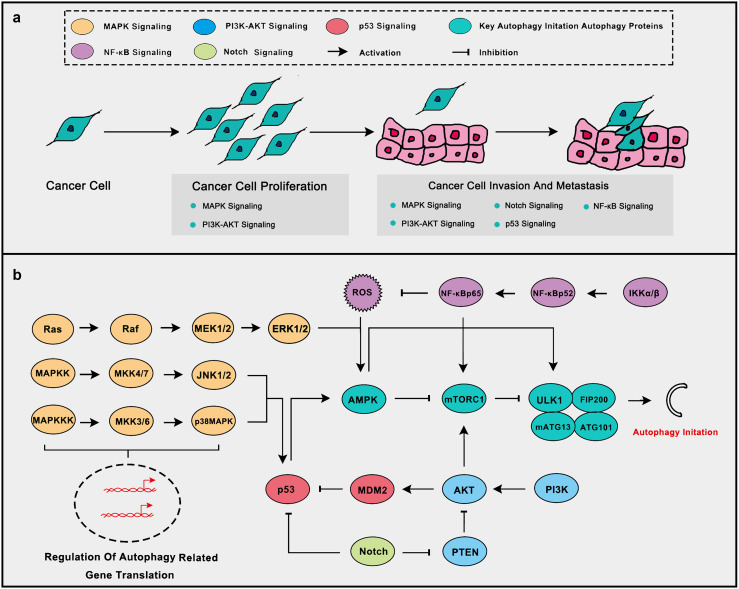
Fig. 1.
Some oncogenic and tumor suppressive signaling pathways related to tumor progression and autophagy initiate. a Oncogenic and tumor suppressive signaling pathways play important roles in the development of the tumor. Of which MAPK, PI3K-AKT and Notch signaling promotes the malignant process while p53 signaling inhibits it. NF-κB signaling responds to inflammation and ROS to inhibit tumor progression. b Oncogenic and tumor suppressive signaling pathways are closely related to autophagy initiate. MAPK signaling can activate autophagy through AMPK activation and promotion of autophagy-related gene translation. PI3K-AKT signaling inhibits autophagy through mTOR activation and p53 inhibition. Notch signaling inhibits autophagy via p53 and PTEN inhibition. NF-κB signaling inhibits ROS aggregation thus to inhibit autophagy