Fig. 3.
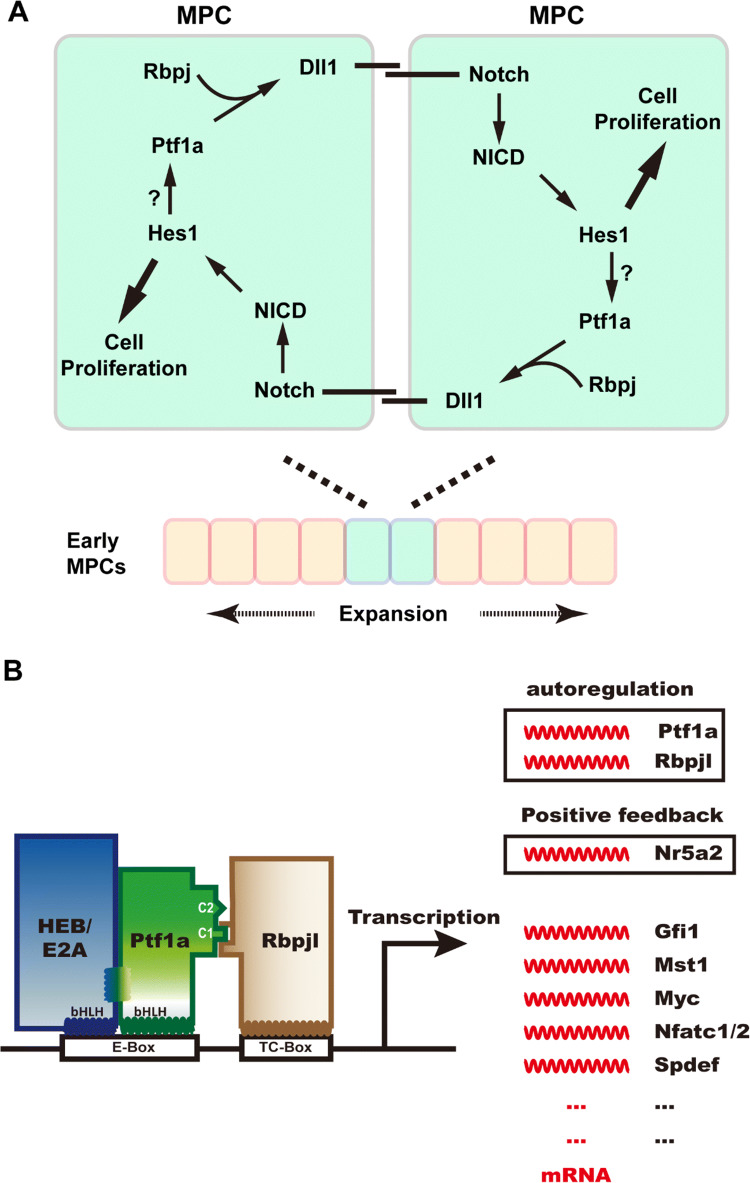
Ptf1a is required for early pancreatic genesis and adult acinar cell identity. a Ptf1a regulates early pancreatic MPC expansion in a positive feed-forward loop (adapted from Ahnfelt-Ronne et al. [38]). Ptf1a and Rbpj activate the expression of Notch ligand Dll1, which in turn binds to Notch receptors on the neighbor MPC, and triggers the downstream pathway of Notch. The activated Notch intracellular domain (NICD) enters the nucleus and activates transcription of target genes such as Hes1, which promotes cell proliferation. Hes1 may also maintain the Ptf1a level by stabilizing the Ptf1a structure. This positive feed-forward mechanism guarantees the proliferation and expansion of early MPCs in pancreatic primordia. b Ptf1a participates not only in the fate specification of acinar cells during development, but also in the maintenance of their physiological function and identity in the adult pancreas. The PTF1 triplex is capable of autoactivation by transactivating Ptf1a and Rbpjl expression. PTF1 activates the expression of Nr5a2 which can positively regulate the expression of Ptf1a and Rbpjl in return. PTF1 also activates the expression of many transcription factors crucial for acinar cell development and function, such as Gfi1, Mst1, Myc, Nfatc1/2, and Spdef