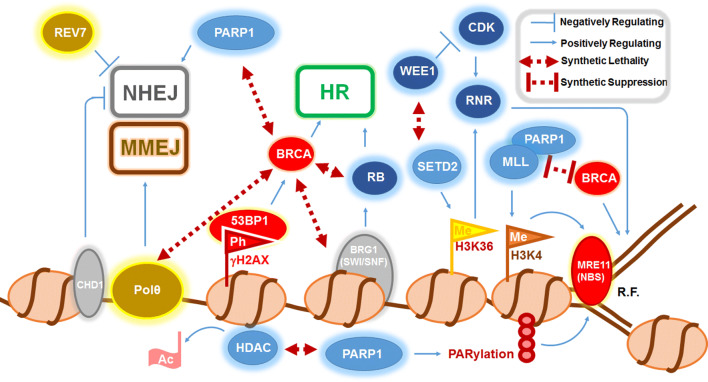
Fig. 3.
The genetic–epigenetic interplay involved in cell cycle regulation and DNA damage repair. Cell cycle regulators are in dark blue (WEE1, CDK, RNR, RB), DNA repair factors in red (BRCA, 53BP1, MRE11, NBS); chromatin remodeling factors in grey (CHD1, BRG1), DNA polymerase-linked factors in yellow (Polθ and REV7), nucleosomes in beige, and chromatin-modifying proteins in light blue (HDAC, PARP1, SETD2, MLL) Flags indicate histone modifications that include phosphorylation (Ph) of histone H2AX (γH2AX), methylation (Me) of histone H3 lysine 4 (H3K4) and histone H3 lysine 36 (H3K36). Many regulators of homologous recombination repair (HR) and non-homologous end joining (NHEJ) and microhomology end joining (MMEJ) show synthetic lethal relationship with BRCA proteins. Abbreviations: R.F. replication fork; Ac acetyl group; RNR ribonucleotide reductase; CDK cyclin-dependent kinase; RB retinoblastoma protein; HDAC histone deacetylase; PARP1 poly (ADP) ribose polymerase 1; MLL mixed lineage leukemia; NBS Nijmegen Breakage Syndrome; Polθ polymerase θ. Double-headed maroon lines indicate interconnecting factors that showed synthetic lethality or suppression upon downregulation. Blue lines represent an induction (positively regulating) and repression (negatively regulating)