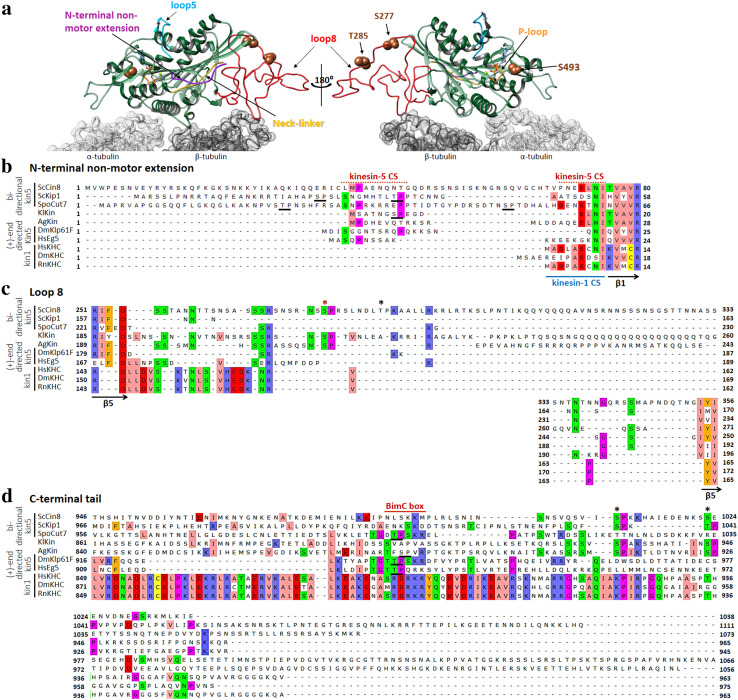
Fig. 3.
Structural features that affect the directionality of kinesin-5 motors. a A Cin8 motor bound to αβ-tubulin dimer. The model of Cin8 motor domain is super-imposed on the cryo-electron microscopy structure of a S. pombe Cut7 motor domain-decorated MT in the AMP-PNP-bound state (PDB: 5M5I) [128]. Except for the non-motor N-terminal extension, the structure of Cut7 was omitted from the overlay for clarity. α- and β-tubulin subunits are indicated in light and dark gray, respectively. The structural elements are highlighted in different colors, with the Cut7N-terminal extension in purple, the ATP-binding p-loop in orange, loop 5 in cyan, Cin8-specific loop 8 in red, the neck linker in yellow and the three Cdk1 phosphorylation site S277, T285 and S493 as brown spheres. The Cin8 model was created using the homology modelling Swiss-Model server [152], while the superimposition and molecular graphics were performed with UCSF Chimera [155]. b–d Amino acid sequence alignments of seven kinesin-5 homologs (top seven sequences) and three kinesin-1 homologs (bottom three sequences). Organisms are indicated on the left: Sc: Saccharomyces cerevisiae, Spo: Schizosaccharomyces pombe, Kl: Kluyveromyces lactis, Ag: Ashbya gossypii, Dm: Drosophila melanogaster, Hs: Homo sapiens, Rn: Rattus norvegicus. Numbers represent amino acid positions in the sequence of each homolog. The sequences were aligned using Unipro UGENE software and adjusted to align the consensus secondary structure elements depicted at the bottom of each alignment. The threshold for consensus residue highlighting was fixed at 30%. The directionalities of kinesin-5 proteins are represented on the left, and although the directionalities of KlKin and AgKin are unknown, they are included here as they contain the loop 8 insertion, similar to ScCin8. The UniProt ID of the sequences are: ScCin8–P27895, ScKip1–P28742, SpoCut7–P24339, KlKin–Q6CSH2, AgKin–Q8J1G7, DmKlp61F–P46863, HsEg5–P52732, HsKHC–P33176, DmKHC–P17210, RnKHC–Q2PQA9. b N-terminal non-motor extension. The first β-strand of the catalytic domain (β1) is indicated on the bottom. The nine residues that can form a β-sheet while interacting with the docked neck linker and form a neck cover strand (CS) in kinesin-1 motors [124] are indicated as kinesin-1 CS. The kinesin-5-specific N-terminal region that was shown to function as a CS [96, 99] is indicated above as kinesin-5 CS. The isoelectric pH values for the N-terminal extensions were calculated as follows: ScCin8—9.47, ScKip1–11.42, SpoCut7—9.39, KlKin—3.57, AgKin—4.58, DmKlp61F—9.99, HsEg5—9.82, HsKHC—3.67, DmKHC—4.00, RnKHC—3.67. The unique Cdk1 sites present in ScKip1, SpoCut7 and KlKin are underlined. The roles of these sites are unknown. The Cin8 sequence starts from methionine at position − 39, relative to the first methionine indicated in electronic databases, since previous publications reported that Cin8 is expressed from – 39M [106, 107, 111, 133], indicated here as the first methionine, M1. c Loop 8, with red and black asterisks indicating the conserved and non-conserved Cdk1 phosphorylation sites, respectively. The bordering β-strands are indicated at the bottom. d The C-terminal tail domain. The BimC boxes containing the Cdk1 phosphorylation site are underlined. Other Cdk1 sites are indicated by asterisks