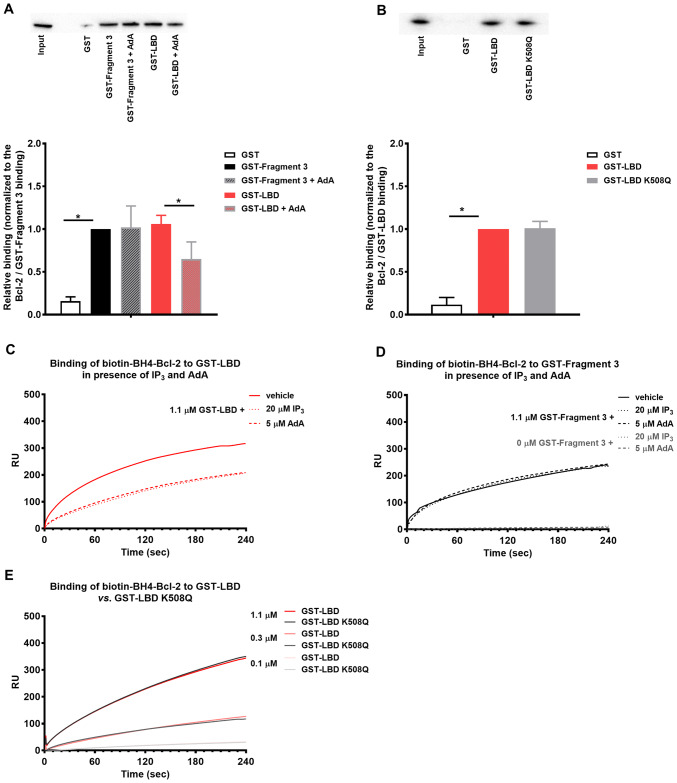
Fig. 7.
Bcl-2 and its BH4 domain compete with IP3 and AdA for LBD, but they do not occupy the exact same site. a Representative GST-pull down experiments for assessing the effect of AdA (5 μM) on the binding of 3xFLAG-Bcl-2 from COS-1 cell lysate to GST-fused IP3R1 fragments corresponding to the Fragment 3 and LBD. The samples were analyzed via Western blot and stained with anti-FLAG antibody. 0.2 μg of total COS-1 lysates was used as input. The immunoreactive bands from three independent experiments, utilizing each time independently transfected cells and freshly prepared lysates, were quantified and normalized to the binding of 3xFLAG-Bcl-2 to GST-Fragment 3, which was set as 1. The data are plotted as mean ± SEM. b Representative GST-pull down experiments for comparison of the binding of 3xFLAG-Bcl-2 from COS-1 cell lysate to GST-LBD and GST-LBD K508Q. The samples were analyzed via Western blot and stained with anti-FLAG antibody. Total COS-1 lysates (1 μg) were used as input. The immunoreactive bands from three independent experiments, utilizing each time independently transfected cells and freshly prepared lysates, were quantified and normalized to the binding of 3xFLAG-Bcl-2 to GST-LBD, which was set as 1. The data are plotted as mean ± SEM. *Stands for p < 0.05. c, d Representative sensorgrams of the surface plasmon resonance experiments expressed in RU as a function of time. The biotin-BH4-Bcl-2 peptide and the scrambled peptide were immobilized on different channels of a streptavidin-coated sensor chip. The channels on the chip were exposed to 1.1 µM purified GST-LBD (c) or 0 and 1.1 μM GST-Fragment 3 d of IP3R1 in presence of IP3 (20 µM) or AdA (5 µM). e The channels on the chip were exposed to different concentrations of GST-LBD or mutated GST-LBD K508Q, which fails to bind IP3