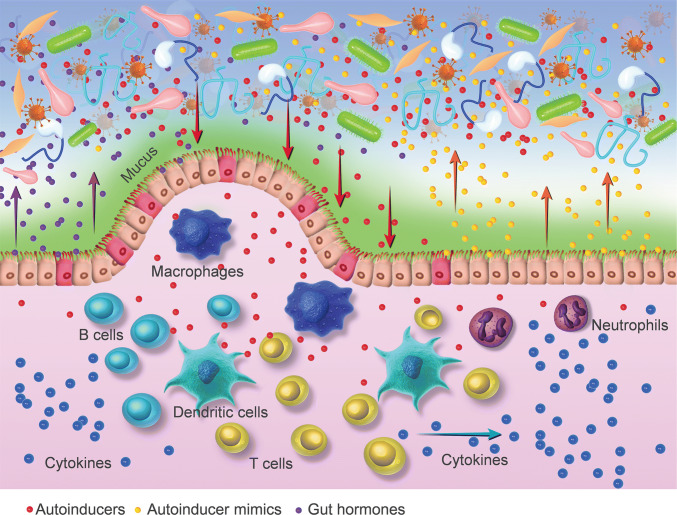
Fig. 2.
Inter-kingdom signaling between gut microbiota and their host. Autoinducers of gut microbiota talk to the host’s gut by eliciting proinflammatory effects and modulating the activities of T lymphocyte, macrophage, dendritic cells and neutrophils. The gut mucosa interferes with bacterial autoinducers by secreting autoinducer mimics. Bacterial autoinducers and gut hormones epinephrine and noradrenaline may be interchangeable in the crosstalk between the microbiota and human gut