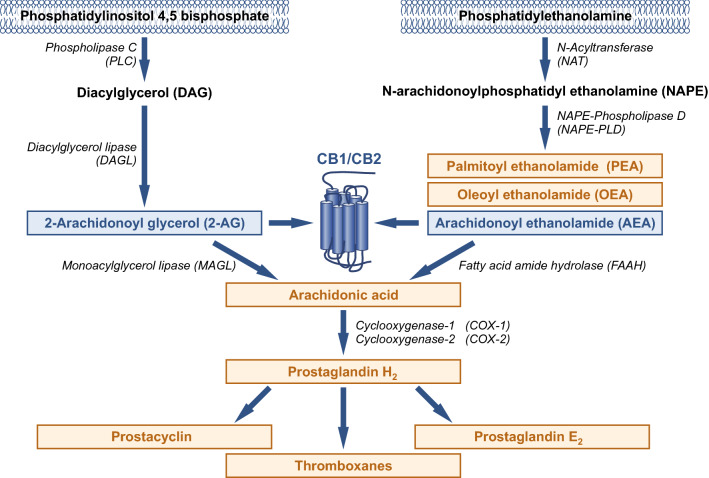
Fig. 1.
Pathways involved in the formation and degradation of endocannabinoids (in blue) and other bioactive lipids (orange). Endocannabinoids are synthesized from plasma membrane phospholipids. A major pathway of AEA synthesis requires N-acyltransferase (NAT) and NAPE-phospholipase D (NAPE-PLD). 2-AG involves phospholipase C (PLC) and diacylglycerol lipase (DAGL) enzymes. The biosynthesis pathway of AEA is the same as for the anti-inflammatory palmitoylethanolamide (PEA) and the anorexigenic oleoyl ethanolamide (OEA). The degradation of AEA and 2-AG by fatty acid amide hydrolase (FAAH) and monoacylglycerol lipase (MAGL), respectively, results in arachidonic acid (AA), which can be converted by cyclooxygenase into eicosanoids, such as prostaglandins, prostacyclins, and thromboxanes