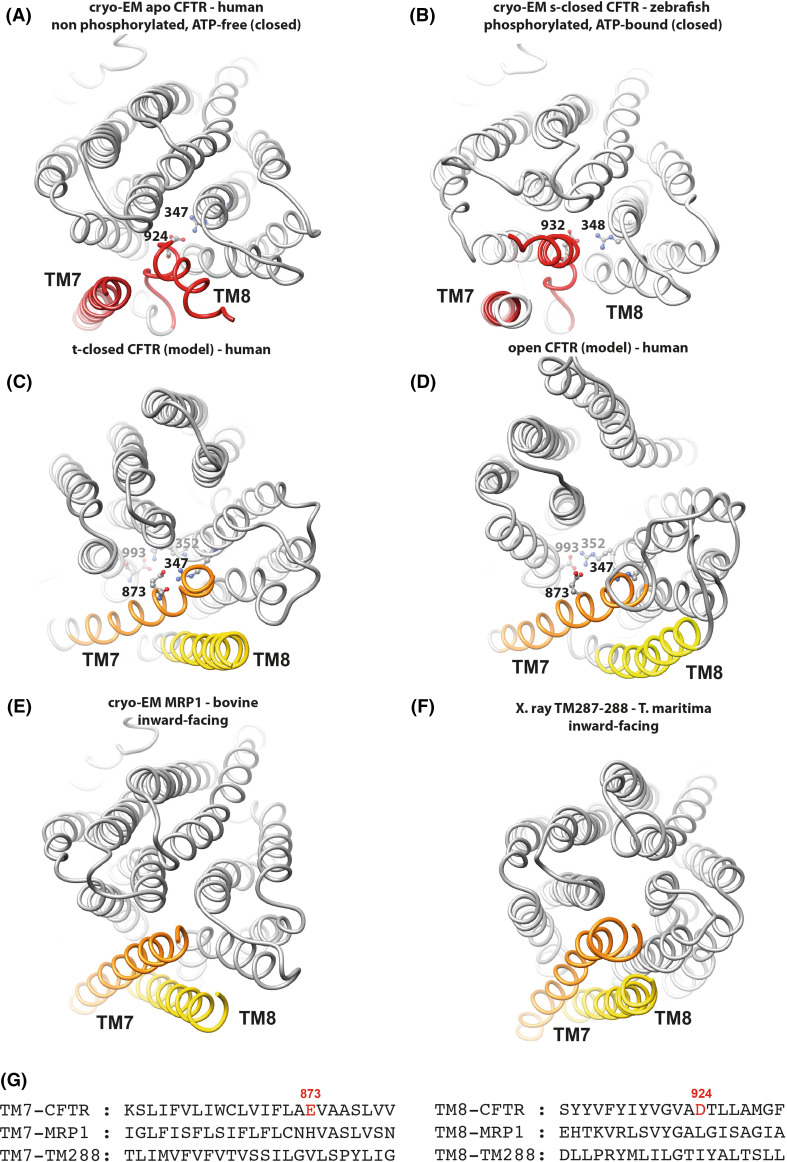
Fig. 6.
The TM7-TM8 pair. Comparison of 3D structures, viewed from the extracellular side, of the membrane-spanning domains (MSDs) of CFTR from cryoEM 3D structures in closed conformations [a apo, quiescent form (human): PDBID:5UAK [7]. b s-closed form (zebrafish): PDBID:5W81 [8]. Amino acid (aa) 932 is equivalent to human CFTR aa 924, aa 348 to human CFTR347)] and from human CFTR 3D structure models in a t-closed form (c) and in an open form (d) [14]. These 3D structures were compared to two experimental 3D structures in inward-facing conformations (e bovine MRP1, PDBID:5UJ9 [52]; f T. maritima TM287/288, PDBID:4Q4A) [53], highlighting the atypical position of the TM7–TM8 helices in the two cryo-EM CFTR 3D structures. Amino acids participating in salt bridges in the different conformations are shown in a ball-and-stick representation (also see Supplementary Data 5). g Structural alignment of the sequences of the CFTR, MRP1, and TM288 TM helices 8 and 7, highlighting specific features in the CFTR sequence