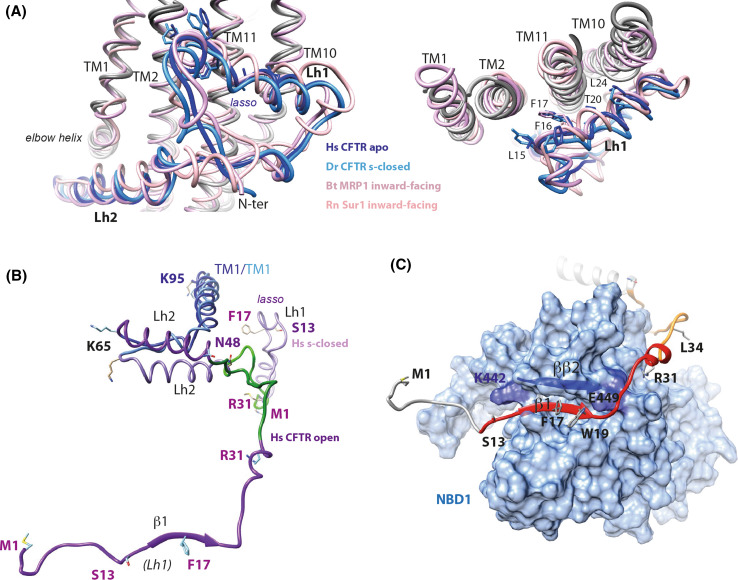
Fig. 8.
Structures of the CFTR N-terminal extension: the lasso and a possible, alternate conformation. a Superimposition of the lasso conformations of the N-terminal extension of CFTR, in an apo, ATP-free state [human (Hs) CFTR apo [7], PDBID:5UAK, dark blue], in the s-closed, ATP-bound state [zebrafish (Dr) CFTR s-closed [8], PDBID:5W81, light blue], in the N-terminal extension of bovine (Bt) MRP1 [52], (PDBID:5UJA, dark pink) and in rat (Rn) SUR1 [68], (PDBID:5TWV, light pink). Two orthogonal views are displayed, highlighting the particular conformation of this sequence segment (left) and its contacts with TM1-TM2 and TM10-TM11 (right). b Structure of the CFTR N-terminal extensions (light purple) in the human s-closed conformation (“lasso”) and, as hypothesized, in the open conformation (dark purple, this study after 20 ns MD simulation). This view was done after superimposition of parts of the TM1 helices (blue, aa 65–95, RMSD 2.88 Å on 31 Cα positions). The lasso segment encompassing aa 32–48 was rotated around aa N48, in its native conformation, leading to directly allow the association of strands β1 and NBD1 ββ2, before MD simulation. c View of the contacts that the CFTR N-terminal region is proposed to make with NBD1 (solvent accessible surface in light blue; aa 382–645, with strand ββ2 highlighted in dark blue). The segments that were experimentally shown to make weak and strong contacts with a NBD1 construct (aa 373–589) are shown in orange and red, respectively [82]