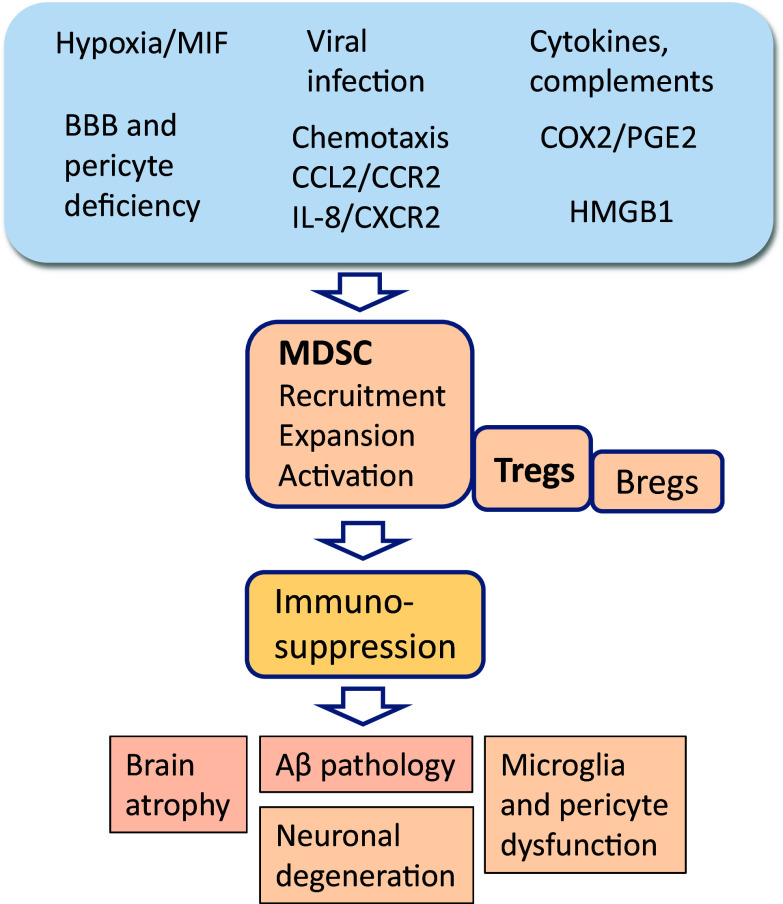
Fig. 3.
Potential mechanisms which could promote immunosuppression and maintain chronic inflammation in AD brains through the recruitment and activation of MDSCs. Hypoxia and viral infections, probable causes of AD, are strong inducers of the accumulation of MDSCs into the brain. It is known that inflamed AD brains secrete several chemokines which trigger the chemotaxis of MDSCs into the brain. Consequently, several cytokines and complements as well as prostaglandin PGE2 and alarmin HMGB1 stimulate the immunosuppressive functions of MDSCs in AD brains. Sustained MDSC activity provokes chronic inflammation involving the deposition of Aβ, increases brain atrophy, and, finally, leads to neuronal degeneration